Maharashtra board class 10 science chapter 8 metallgury textbook solutions
So, to enhance your chances of board exams the this solutions will help you, here we have compiled the all the Textbook solutions for class 10 science chapter 8 metallgury textbook solutions
In this article. You can get all the Questions and answers of Class 10 science chapter 8 metallgury textbook solutions along-with Simple Answers of the each questions.
ybstudy.com class 10 science textbook solutions is of high class and very high quality; it will benefit all our students of class 10 very much.
This solutions are 100% accurate and updated study material for all as per the maharashtra state board Textbook.
Question 1: Write names.
a. Alloy of sodium with mercury.
Answer : Sodium amalgam, commonly denoted as Na(Hg), it is an alloy of mercury and sodium.
b. Molecular formula of the common ore of aluminium.
Answer : Bauxite(Al2O3.2H2O) is the common ore of aluminium.
c. The oxide that forms salt and water by reacting with both acid and base.
Answer : Metal oxides which react with both acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are also known as amphoteric oxides. For example: Al2O3 is an amphoteric oxide. An amphoteric compound is a molecule or ion that can react both an acid as well as a base to produce salt and water.
d. The device used for grinding an ore.
Answer : The device used for grinding an ore is grinding mill.
e. The nonmetal having electrical conductivity.
Answer : Graphite an allotrope of carbon is a good conductor of electricity.
f. The reagent that dissolves noble metals.
Answer : Aqua regia is 1:3 mixture of concentrated nitric and hydrochloric acids. It dissolves noble metals such as gold, palladium, and platinum.
Question 2: Make pairs of substances and their properties
Substance. Property
A. Potassium bromide. 1.Combustible
B. Gold. 2. Soluble in water. C. Sulphur. 3. No chemical reaction.
D. Neon. 4. High ductility.
Answer :
Substance. Property
A.Potassium bromide 1. Soluble in water
b. Gold. 2. High ductility. C.Sulphur. 3. Combustible.
D. Neon. 4. No chemical reaction
Question 3: Identify the pairs of metals and their ores from the following.
Group A. Group B
A. Bauxite. 1. Mercury.
B. Cassiterite. 2. Aluminium.
C. Cinnabar. 3. Tin
Answer :
Group A. Group B
A. Bauxite. 1. Aluminium
B. Cassiterite. 2.Tin
c. Cinnabar. 3. Mercury
Question . 4 Explain the terms.
A. Metallurgy
Answers : Metallurgy defined as extraction of metal from their pure form. metals are commercially extracted from minerals at low cost and minimum efforts.
These minerals are called ores.
The steps involved in extraction of metals
1. Crushing or grinding
2.concentration of ores
3. Conversation of concentrated one into metal.
4. Purification of impure metals.
B. Ores
Answers -:– metals are commercially extracted from minerals at low cost and minimum efforts .
These minerals are called ores. ores are raw materials for making metals.
C. Minerals
Answers -: The compounds of metals that occur in nature along with the impurities are called minerals.
- minerals are the natural source in which the metals and their compounds are found in earth.
- all minerals are not ores but all ores are minerals.
D. Gangue
Answers -: The impurities present in the one such as sand , rocks etc are known as gangue.
Question no. 5 Write scientific reasons.
a. Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Answer :
- Copper reacts with carbon dioxide in the air to form copper carbonate.
- As a result, copper loses its shiny brown surface forming a green layer of copper carbonate.
- The citric acid present in the lemon or tamarind neutralizes the basis copper carbonate and dissolves the layer.
- Therefore, greenish copper vessels are cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice to give luster to the surface of the copper vessel.
b. Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Answer-:
- Ionic compounds are mostly solids and are packed in a crystal lattice structure .
- They have strong electrovalent bonds between the constituent atoms and stronger the bonds heigher is the melting point .
- this kind of packing of the atoms , their melting point is quite high . Ex: Nacl , KCl
c. Sodium is always kept in kerosene.
Answer-:
1) Sodium are very reactive metals and kept in kerosene oil to prevent it from coming in contact with oxygen and moisture as they react to form their hydroxides.
2) This is an exothermic reaction and lot of heat is generated so both the metals are kept in kerosene oil.
d. Pine oil is used in froth flotation.
Answers -:
1) pine oil consists mainly of cyclic terpene alcohols.
2) pine oil is used in froth flotation process because it does not have affinity towards water and it attracts impurities which can be washed away.
e. Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
Answer :
- Anodes needs to be replaced during the electrolysis of the Alumina because they gets oxidized.
- During the Electrolysis of the Alumina, Oxygen is deposited at the anode.
- Now, Anode is made up of the graphite (or Carbon), thus carbon reacts with the Oxygen and forms its oxide.
- As a result of this Oxidation, we needs to replace the anode from time to time.
Question 6 : When a copper coin is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a glitter appears on the coin after some time. Why does this happen? Write the chemical equation.
Answer :
- Copper is more reactive than silver. Hence displacement reaction occurs.
- When copper coin is dipped in silver nitrate solution forming copper nitrate and silver metal.
- A shining white deposit of silver metal is formed on copper coin. Hence, she saw a silver shine on the copper coin
- Balanced equation:- 2AgNO3(ag)+Cu(s)→Cu(NO3)2(ag)+2Ag(s)
Question 7: The electronic configuration of metal ‘A’ is 2,8,1 and that of metal ‘B’ is 2,8,2. Which of the two metals is more reactive? Write their reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer :
1) moving from left to right in a period of periodic table, the chemical reactivity of elements first decreases from sodium to silicon and then increases from phosphorus to chlorine.
2) The electronic configuration of metal ‘A’ is 2,8,1. This is electronic configuration of sodium metal.
3) The electronic configuration of metal ‘B’ is 2,8,2. This is electronic configuration of magnesium metal.
4) In the first element of third period, sodium, there is 1 valence electron which it can lose easily to react with other substances, so it is very reactive metal.
5) The second element magnesium has 2 valence electrons. It is not easy for an atom to lose 2 electrons, so magnesium is less reactive than sodium.
Reaction with dil hydrochloric acid:
Na + HCl → NaCl + H2Mg + HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Question 8: Draw a neat labelled diagram.
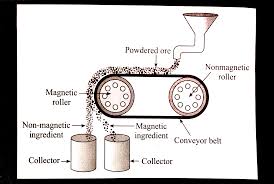
a. Magnetic separation method.
Answer :
b. Froth floatation method.
Answer :
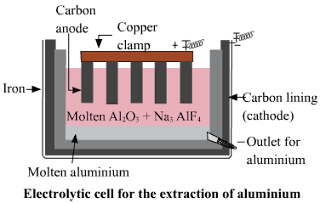
c. Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer :
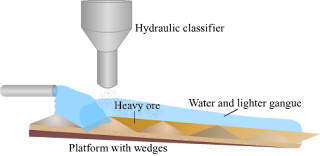
d. Hydraulic separation method.
Answer :
Question 9: Write chemical equation for the following events.
a. Aluminium came in contact with air.
Answer-:
- Aluminum is a very reactive metal.
- The outer surface of the metal is actually covered by a very thin layer of the oxide which keeps the metal protected from the air. But when the oxide layer is damaged, aluminum comes in contact with the air.
- It is easily attacked by air. Then aluminium starts reacting with the oxygen. It will burn as bright white flame to change into aluminum(III) oxide.
Chemical Equation:
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
b. Iron filings are dropped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Answer-:
1) iron is more reactive than copper.
2) it is displacement reaction in which iron displace copper sulphate in the reaction.
3) colour of the solution slowly changes from blue to green due to formation of iron sulphate.
Chemical equation -:
Fe + CuSO4 ——- Cu + FeSO4
c. A reaction was brought about between ferric oxide and aluminium.
Answer-:
1) Aluminium is more reactive than iron.
2) Aluminium metal replaces iron from ferric oxide to form aluminium oxide and iron.
Chemical Equation:
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe
d. Electrolysis of alumina is done.
Answer-:
1) The electrolysis of alumina is carried out in a steel tank lined inside with graphite.
2) The graphite lining serves as cathode.
3) Anode is also made up of graphite rods hanging in the molten mass.
4) The electrolyte consists of alumina dissolved in fused Cryolite(Na3AlF6) and Fluorspar(CaF2).
5) Cryolite lowers the melting point of alumina and fluorspar increases the fluidity of the mass so that the liberated aluminum metal may sink at the bottom of the cell.
6) When electric current is passed through this mixture, the aluminum is collected at the cathode in molten state and sinks at the bottom.
Chemical equation :
Ionization of Alumina:
2Al2O3 → 6O-2 + 4Al+3
Reaction at Cathode:
4Al+3 + 12e- → 4Al
Reaction at Anode:
6O-2 → 3O2 + 12e-,
C + O2 → CO2
e. Zinc oxide is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid.
ANSWER:-
1) This is a double displacement reaction.
2) Zinc Oxide is an inorganic compound with formula ZnO.
3) It is insoluble in water.
4) When Zinc oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid it forms zinc chloride and water.
5) It also leads in the formation of small bubbles of hydrogen.
Chemical Equation:
ZnO + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O.
Question 10: Complete the following statement using every given options.
During the extraction of aluminium…………..
a. Ingredients and gangue in bauxite.
Answer : Bauxite is the main ore of aluminium. Silica (SiO2), ferric oxide (Fe2O3) and titanium oxide (TiO2) are the impurities present in bauxite.
b. Use of leaching during the concentration of ore.
Answer : Separation of these impurities is done by leaching process using either Bayer’s method or Hall’s method
c. Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
Answer :
1) In the Hall’s process the bauxite is in powdered form and then leached by heating with aqueous sodium carbonate in the digester to form water soluble sodium aluminate.
2) Then the insoluble impurities are filtered out.
3)The filtrate is warmed and neutralised by passing carbon dioxide gas through it. This results in the precipitation of aluminium hydroxide.
Al2O3 2H2O (s) + Na2CO3 (aq) →2NaAlO2 (aq) + CO 2 + 2 H2O (l)
2NaAlO2 (aq) + 3H2O + CO2 (g)→ 2Al(OH)3 + Na2CO 3
The precipitate of Al(OH)3 obtained in both, Bayer’s and Hall’s processes is filtered, washed, dried and then calcined by heating at 10000C to obtain alumina.
2Al(OH)3 → Al2O3 + 3H2O
d. Heating the aluminium ore with concentrated caustic soda.
Answer : When aluminium ore is heated with caustic soda( NaOH) solution under high pressure for 2 to 8 hours at water soluble sodium aluminate is formed.
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Question 11: Divide the metals Cu, Zn, Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, Li into three groups, namely reactive metals, moderately reactive metals and less reactive metals.
Answer :
Highly moderately. Less
reactive reactive reactive
metals metals Metals
Ca Fe Au
Mg Zn Ag
Na Cu Pt
Li