Class 6 chapter 5- Substances in the Surroundings
Maharashtra State Board Science Textbook Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 5 – Substances in the Surroundings: Their States and Properties are extremely important for helping students understand complex scientific concepts in a simple and clear manner. These Class 6 chapter 5- Substances in the Surroundings Textbook Solutions are a valuable resource for preparing for school-level exams and also help lay a strong foundation for various competitive entrance examinations in the future. Studying the Class 6 Science answers not only boosts your understanding of key topics but also helps you evaluate your strengths and identify areas that need improvement.
We provide step-by-step solutions for every question from Chapter 5 to help you understand the logic behind the answers, making it easier to apply similar concepts to other science problems. Our material also includes a worksheet for Class 6 Science Chapter 5, extra questions, and detailed Maharashtra State Board solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5. If you need the Class 6 Science Chapter 5 PDF, feel free to contact us. These resources make learning interactive and efficient, especially when preparing for unit tests, school exams, or final board exams.

In addition, we also cover Class 6 Chapter 4 solutions, so you have complete access to consecutive chapters for continuous learning. All solutions are regularly updated based on student feedback and exam trends to ensure you’re studying the most accurate and updated content. By using our Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Substances in the Surroundings: Their States and Properties solutions, students gain confidence, clarity, and better performance in exams—all at no cost.
Important points to remember
- When a substance changes from one state to another, the process is called change of state of the substance.
- Solids, liquids and gases are the three states of substances.
- The temperature of a substance, (how hot or cold it is), can be measured with the help of a thermometer.
- Heat is the cause of the change of state of substances.
- Substances have various properties like hardness, elasticity, brittleness, fluidity, density, solubility and transparency.
- Metals form a separate group of substances.
- Metals have some common properties like malleability, ductility, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, sonority, lustre, and characteristic colour.
Class 6 chapter 5- Substances in the Surroundings Textbook Solutions
Question 1: In the paragraph below, write ‘solid’, ‘liquid’ or ‘gas’ in each of the brackets depending on the substance referred to just before.
On a bright sunny day, Riya and Gargi are playing with a ball ( ) in the park. Gargi feels thirsty. So, Riya brings tender coconut water ( ) for her. At the same time, a strong breeze ( ) starts blowing and it also begins to rain ( ). They run back into the house ( ), change their clothes ( ) and then their mother gives them a cup ( ) of hot milk ( ) to drink.
Answer: On a bright sunny day, Riya and Gargi are playing with a ball (solid) in the park. Gargi feels thirsty. So, Riya brings tender coconut water (liquid) for her. At the same time, a strong breeze (gas) starts blowing and it also begins to rain (liquid). They run back into the house (solid), change their clothes (solid) and then their mother gives them a cup (solid) of hot milk (liquid) to drink.
Question 2: Discuss
a) Riya pours some water from her bottle into another bottle. Does it change the shape of the water ?
Answer: Yes, the shape of the water will change because liquids do not have a shape of their own. They take the shape of the container in which they are present.
b) Halima picks up a small stone from the ground and puts it in the water in a dish. Does the shape of the stone change ?
Answer : No, the shape of the stone will not change by putting it in a dish containing water because solids have definite shape. They do not change their shape and retain it, no matter whatever be the circumstances.
Question 3: Write the properties of these substances.
Water, glass, chalk, iron ball, sugar, salt, flour, coal, soil, pen, ink, soap.
Answer:
Water- Fluidity
Glass- Transparent, brittle
Chalk- Brittle
Iron ball- Hardness
Sugar- Solubility
Salt- Solubility
Flour-Solubility
Coal- Brittle
Soil- Solubility
Pen- Hard
Ink- Fluidity
Soap- Brittle
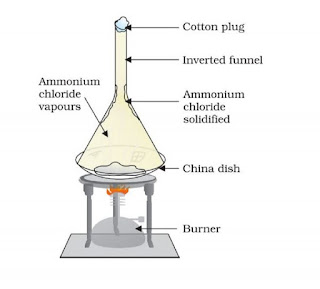
Question 4: What is sublimation? Write the names of everyday substances that sublimate.
Answer : Sublimation is the change of the gaseous state directly into the solid state, without going through the liquid state, and vice versa.
Examples of sublimation:- dry ice, moth balls or napthalene balls, camphor (kapur).
Question 5: What is it made from? Why?
a) A sickle to cut sugarcane.
b) The sheets used for roofing.
c) A screwdriver
d) A pair of tongs.
e) Electric cables.
f) Ornaments.
g) Pots and pans.
Answer :
a) A sickle to cut sugarcane– Made out of iron since it is very hard and strong.
b) The sheets used for roofing– Aluminium is used to make sheets for roofing because it is malleable i.e. it can be hammered into sheets.
c) A screwdriver– It is made up of steel beacuse it is very hard and duable.
d) A pair of tongs– They are made up of metals like iron or aluminium beacuse they have high melting points and do not melt while using on flames.
e) Electric cables– Metals like silver, gold, copper and platinum are used to make wires because they are ductile i.e. they can be drawn into wires.
f) Ornaments– Metals such as gold and silver are used for making jewellery because they are very lustrous.
g) Pots and pans– Copper is used to make pots and pans because it is a good conductor of heat.
Question 6: What will happen if….? And why?
a) Nails are made of plastic
Answer: If nails are made out of plastic, they cannot be used for its usual purposes. They could not be hammered like iron nails and ould not possess the strength which iron nails have. It means they would have no strength to hold the things together.
b) A bell is made up of wood ?
Answer: If a bell is made of wood, it will not ring. The bells are made up of metals like copper etc. as they show the property of sonority i.e. the ability to produce a ringing sound when striked upon. Wood does not have this property and hence cannot be used to make bells.
c) Rubber is not fitted on a pair of tongs.
Answer: Tongs are made up of metals and they have the ability to conduct heat. If rubber is attached to the tongs, the heat will be transfered to the rubber and it will melt off.
d) A knife is made of wood.
Answer: Knife is used to cut vegetables, fruits etc. The regular knifes which we use are made up of metals like iron etc. as they are hard, strong and durable. Also they can be sharpened and moulded into shapes which we desire. Knifes made out of wood cannot be used for cutting or chopping purposes.
e) An axe is made of rubber.
Answer: An axe is used to cut and chop wood. It is made up of metals beacause they are stong, hard and durable. Also they can be moulded and sharpened which is an important characteristic. These properties are not applicable to rubber. An axe made of rubber will neither be hard nor sharp enough so that it can be used for its usual purposes.
Question 7: Who am I?
a) I’m found in a thermometer, I measure your temperature.
b) I make things hot or cold.
c) I have no shape whatsoever !
d) I dissolve in water, but not in kerosene.
Answer:
a) I’m found in a thermometer, I measure your temperature- Mercury
b) I make things hot or cold- Temperature
c) I have no shape whatsoever !- Gas
d) I dissolve in water, but not in kerosene- Salt
Question 8: Why does this happen?
a) Coconut oil thickens in winter.
Answer: Coconut oil is made up of two types of fat- saturated and unsaturated fats. It contains 90% saturated fats and 10% unsaturated fats. It remains liquid at higher temperatures but turns into solid as the temperatures drop in winters. This property of coconut oil is attributed to the higher content of saturated fats. Oils like mustard oil, sunflower oil remain liquid even in winters because they contain less amount of saturated fats as compared to coconut oil.
b) Kerosene left open in a dish disappears.
Answer: Kerosene left open in a dish disappears because it is a volatile compound. It quickly evopurates if it is kept in open.
c) The fragrance of incense sticks lighted in one corner of a room spreads to the other corner.
Answer : When the incense stick is lighted, it releases smoke which contains the fragrance. Smoke is a form of gas which quickly spreads in the entire room along with the fragrance and thus making the entire room fragrant.
d) What you see in the picture.
Answer: The picture shows two things which are present in tub of water. One is a balloon which floats on the surface of the water while the other is an apple which sinks to the bottom of the tub. The balloon floats on the surface of the water because it has less denity as compared to the density of the water whereas the apple sinks to the bottom of the tub because it has more density than water.
#Can you Tell (Read this list of substances : Spirit, camphor, petrol, ghee, coconut oil, naphthalene balls, ammonium chloride (navsagar).)
1. Which ones freeze in winter?
Answer: ghee, coconut oil.
2. Which liquid have you seen change into a vapour ?
Answer: petrol, spirit.
3. Which solids directly change into the gaseous state?
Answer: naphthalene balls, ammonium chloride
