NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 – Molecular Basis of Inheritance solutions
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 – Molecular Basis of Inheritance solutions Struggling to find reliable Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 question answers or clear Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Solutions? You’re not alone! This crucial chapter, diving deep into DNA, RNA, replication, transcription, and the genetic code, forms the bedrock of modern biology. Looking for that perfect Molecular Basis of Inheritance Class 12 NCERT PDF containing all the exercise answers explained step-by-step? Or perhaps you need concise Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 PDF Notes for quick revision before exams? Whether it’s downloading the official Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Solutions PDF, accessing a well-structured Molecular Basis of Inheritance exercise answers PDF, or finding comprehensive Molecular Basis of Inheritance questions and answers for practice, this guide is your one-stop solution.
We understand the pressure of board exams and the need for accurate, easy-to-understand resources aligned perfectly with the NCERT textbook. Stop searching endlessly for scattered notes or unreliable solutions. Discover where to access trusted, high-quality NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 PDF download links and supplementary notes that break down complex concepts like the Lac Operon or DNA fingerprinting into simple terms. Get ready to clarify doubts, strengthen your understanding, and boost your confidence for this essential unit!

Important Points to Remember:
- Nucleic acids are long polymers of nucleotides. While DNA stores genetic information, RNA mostly helps in transfer and expression of information.
- Though DNA and RNA both function as genetic material, but DNA being chemically and structurally more stable is a better genetic material. However, RNA is the first to evolve and DNA was derived from RNA. The hallmark of the double stranded helical structure of DNA is the hydrogen bonding between the bases from opposite strands. The rule is that
- Adenine pairs with Thymine through two H-bonds, and Guanine with Cytosine through three H-bonds. This makes one strand complementary to the other.
- The DNA replicates semiconservatively, the process is guided by the complementary H-bonding. A segment of DNA that codes for RNA may in a simplistic term can be referred as gene.
- The coding sequences, exons, are interrupted by non-coding sequences, introns. Introns are removed and exons are joined to produce functional RNA by splicing.
- Thebmessenger RNA contains the base sequences that are read in an combination of three (to make triplet genetic code) to code for an amino acid. The genetic code is read again on the principle of complementarity by tRNA that acts as an adapter molecule. There are specific tRNAs for every amino acid. The tRNA binds to specific amino acid at one end and pairs through H-bonding with codes on mRNA through its anticodons. The site of translation (protein synthesis) is ribosomes, which bind to mRNA and provide platform for joining of amino acids. One of the rRNA acts as a catalyst for peptide bond formation, which is an example of RNA enzyme (ribozyme).
- In bacteria, more than one gene is arranged together and regulated in units called as operons. Lac operon is the prototype operon in bacteria, which codes for genes responsible for metabolism of lactose.
- Human genome project was a mega project that aimed to sequence every base in human genome. This project has yielded much new information.
- DNA Fingerprinting is a technique to find out variations in individuals of a population at DNA level. It works on the principle of polymorphism in DNA sequences. It has immense applications in the field of forensic science, genetic biodiversity and evolutionary biology.
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 – Molecular Basis of Inheritance solutions
As the days are nearing for the Board examination, we are starting Online All India NCERT Textbook Solution series program for class 12 Students. It is the ultimate preparation kit to prepare yourself for the upcoming board examination exam. It is unique & different as it not only tests your knowledge but also helps you evaluate your performance on a real-time against other Students rank who take the test from all across the country. Below in this Page, you can get the complete NCERT Solution for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance which is presented in a very well-structured format. Then You can easily Solve the Questions of NCERT Syllabus.
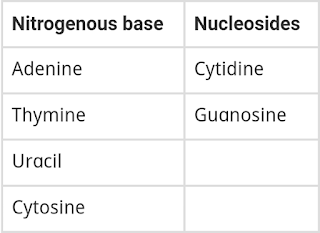
1 Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine.
Answer :
2. If a double stranded DNA has 20 per cent of cytosine, calculate the percent of adenine in the DNA.
Answer : As per Chargaff’s rule, DNA molecules are required to have an equal ratio of purine(adenine and guanine) and pyridine(cytosine and thymine). This is to say that the number of adenine molecules is equivalent to the cytosine molecule. i.e. A = T and G = C.
If dsDNA has 20% of cytosine, then according to the law, it would have 20% of guanine. The remaining 60% represents both A + T molecule. Since adenine and guanine are always present in equal numbers, the percentage of adenine molecule is 30%. And 30% of Thymine molecules
So, the correct answer is of the question is ‘30%’.
3. If the sequence of one strand of DNA is written as follows:
5′-ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC-3′
Write down the sequence of complementary strand in 5’→3′ direction.
Answer : The sequence of complementary strand in 5’→3′ direction is written as:
5′ – GCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCAT – 3′
4. If the sequence of the coding strand in a transcription unit is written as follows:
5′-ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC-3′
Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Answer : As we all know in RNA thymine is replaced by uracil. same as in mRNA, uracil replaces thymine. Hence, the mRNA sequence is as written below:
5′ -AUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGC-3′
5. Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesise semi-conservative mode of DNA replication? Explain.
Answer : Watson and Crick observed that the two strands of DNA are anti-parallel and complementary to each other with respect to their base sequences. This type of arrangement in DNA molecule led to the hypothesis that DNA replication is semi-conservative. It means that the double stranded DNA molecule separates and then, each of the separated strand acts as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. As a result, each daughter DNA molecule would have one parental strand and a newly synthesized daughter strand.
Since only one parental strand is conserved in each daughter molecule, it is known as semi-conservative mode of replication. The The scheme suggested that the two strands would separate and act as a template for the synthesis of new complementary strands. After the completion of replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesised strand. This scheme was termed as semiconservative DNA replication
6. Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), list the types of nucleic acid polymerases.
Answer : Nucleic acid polymerases catalyze the formation of DNA or RNA from nucleoside-triphosphate precursors. As we know Polymerases are the enzymes which are required for the reproduction, maintenance and expression of the genomes of all organisms, including viruses.
The list includes two different types of nucleic acid polymerases:
1. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases
2. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases
1) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase enzyme adds deoxyribonucleotides to synthesize DNA using the base sequence of parental DNA strand by the process of DNA replication.
2) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase: It adds ribonucleotides primer strand to synthesize RNA using the base sequence of template DNA strand.
7. How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?
Answer : The unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the
experiments of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase (1952). They worked with viruses that infect bacteria called bacteriophages. The bacteriophage attaches to the bacteria and its genetic material then enters the bacterial cell. The bacterial cell treats the viral genetic material as if it was its own and subsequently manufactures more virus particles. Hershey and Chase worked to discover whether it was protein or DNA from the viruses that entered the bacteria.
They grew some viruses on a medium that contained radioactive phosphorus and some others on medium that contained radioactive sulfur. Viruses grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA but not radioactive protein because DNA contains
phosphorus but protein does not. Similarly, viruses grown on radioactive sulfur contained radioactive protein but not radioactive DNA because DNA does not contain sulfur.
Radioactive phages were allowed to attach to E. coli bacteria. Then, asnthe infection proceeded, the viral coats were removed from the bacteria by agitating them in a blender. The virus particles were separated from the bacteria by spinning them in a centrifuge. Bacteria which was infected with viruses that had radioactive DNA were radioactive, indicating that DNA was the material that passed from the virus to the bacteria. Bacteria that were infected with viruses that had radioactive proteins were not radioactive. This indicates that proteins did not enter the bacteria from the viruses. DNA is therefore the genetic material that is passed from virus to bacteria.
8. Differentiate between the followings:
(a) Repetitive DNA and Satellite DNA
Answer : Repetitive DNAs are those parts of DNAs that are present in normal genome of an individual and is consisted of several repeats of either same nitrogen base or a repeat of a particular sequence of DNA that is called a tandem. It is present between two genes that are often seen to differentiate between two genes.
Satellite DNAs are those parts of DNA that are present at end of DNA. Those DNAs are parts which also have repeats of sequences but not like that of repetitive DNA. It has a repetition of one or two base pairs for a considerable number of time. According to number of repetition, there are micro, mini and macro satellite DNAs.
- Repetitive DNA doesn’t show polymorphism while satellite DNA show polymorphism.
- Repetitive DNA can be tandem repeats, interspersed repeats while satellite DNA can be micro-satellite, mini-satellite.
- Repetitive DNA forms light bands while satellite DNA forms small dark bands.
(b) mRNA and tRNA
Answer : mRNA or messenger RNA is the connection between gene and protein, and it is the result of the transcribed gene by RNA polymerase. tRNA or transfer RNA is a cloverleaf shaped RNA molecule and provides specific amino acids to the ribosomes.
- mRNA synthesised in Nucleus. While tRNA symthesized in Cytoplasm.
- mRNA is linear in shape. While tRNA is a cloverleaf shape.
- mRNA is comprised of codons. tRNA is comprised of anticodons.
- In mammals, the size of the mRNA molecules is around 400 to 12, 000 nucleotides (nt). while The size of the molecule of tRNA is 76 to 90 nucleotides (nt).
- mRNA carries genetic information from the nucleus to ribosomes for the synthesis of proteins. tRNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes to assist the protein biosynthesis.
(c) Template strand and Coding strand
Answer : DNA is consist of two strand. One strand of DNA holds the information that codes for various genes, this often known as the template strand or antisense strand (which contains anticodons). The other complementary strand is known as the coding strand or sense strand ( which contains codons )
- Template strant polarity is from 5′ to 3′. While Coding strand polarity is 3′ to 5′.
- Template strand is transcribed into mRNA. And coding strand is not transcribed into mRNA.
- Template strand contains anti-codon. Coding strand contains the only codon.
- Template strand Contain the same nucleotide sequence as the tRNA. Coading strand Contain the complementary nucleotide sequence as the tRNA.
9. List two essential roles of ribosome during translation.
Answer : The ribosome is generally responsible for synthesis of proteins by translating the genetic code transcribed in mRNA into an amino acid sequence. Ribosomes use cellular accessory proteins, soluble transfer RNAs, and metabolic energy to accomplish the initiation, elongation, and termination of peptide synthesis.
Ribosomes are sites where synthesis of proteins occurs from individual amino acids. It consists of two subunits – larger subunit serves as an amino acid binding site whereas smaller subunit attaches to the mRNA forming a protein synthesizing complex.
10. In the medium where E. coli was growing, lactose was added, which induced the lac operon. Then, why does lac operon shut down some time after addition of lactose in the medium?
Answer : The lac operon consists of one regulatory gene (the i gene – here the term i does not refer to inducer, rather it is derived from the word inhibitor) and three structural genes (z, y, and a). The i gene codes for the repressor of the lac operon. The z gene codes for beta-galactosidase (β-gal), which is primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of the disaccharide, lactose
into its monomeric units, galactose and glucose. The y gene codes for permease, which increases permeability of the cell to β-galactosides. The a gene encodes a transacetylase. Hence, all the three gene products in lac operon are required for metabolism of lactose.
In lac operon, lactose acts as an inducer. It binds to the repressor and inactivates it. Once the lactose binds to the repressor, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region. Hence, three structural genes express their product and respective enzymes are produced. These enzymes act on lactose so that lactose is metabolized into glucose and galactose.
After sometime, when the level of inducer decreases as it is completely metabolized by enzymes, it causes synthesis of the repressor from regulator gene. The repressor binds to the operator gene and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon. Hence, the transcription is stopped. This type of regulation is known as negative regulation.
11. Explain (in one or two lines) the function of the followings:
(a) Promoter
Answer : A promoter is a region of DNA where transcription of a gene is initiated. Promoter sequences are typically located directly upstream or at the 5′ end of the transcription initiation site. In prokaryotes, the promoter consists of two short sequences at -10 and -35 positions upstream from the transcription start site.
(b) tRNA
Answer : Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that participates in protein synthesis.
tRNA molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length, that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins.
The two most important parts of a tRNA are its anticodon and the terminal 3’ hydroxyl group, which can form an ester linkage with an amino acid.
(c) Exons
Answer : An exon is the portion of a gene that codes for amino acids.
Or // Exons are the genes which carry the genetic information of a organism.
The mature mRNA consists of exons . Exons usually include both the 5’- and 3’- untranslated regions of mRNA, which contain start and stop codons, in addition to any protein coding sequences.
12. Why is the Human Genome project called a mega project?
Answer: The Human Genome Project was a 13-year project coordinated by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Institute of Health. During the early years of the HGP, the Wellcome Trust (U.K.) became a major partner; additional contributions came from Japan, France, Germany, China and others. The project was completed in 2003.
Human Genome Project (HGP) was called a mega project. Because You can imagine the magnitude and the requirements for the project if we simply define the aims of the project as follows:
- Human genome is said to have approximately 3 x 109 bp, and if the cost of sequencing required is US $ 3 per bp (the estimated cost in the beginning), the total estimated cost of the project would be approximately 9 billion US dollars. Further, if the obtained sequences were to be stored in typed form in books, and if each page of the book contained 1000 letters and each book contained 1000 pages, then 3300 such books would be required to store the information of DNA sequence from a single human cell.
- The enormous amount of data expected to be generated also necessitated the use of high speed computational devices for data storage and retrieval, and analysis. HGP was closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called Bioinformatics.
13. What is DNA fingerprinting? Mention its application.
Answer : Every individual has its unique genetic make-up, which may be called its Fingerprint. The technique developed to identify a person with the help of DNA restriction analysis, is known as DNA profiling or DNA fingerprinting. The technique of DNA finger printing was first given by British geneticist, Dr. Alec Jeffreys in 1984.
DNA fingerprinting technique is based on identification of nucleotide sequence present in this wonder molecule. About 99.9% of nucleotide sequence in all persons, is same. Only some short sequences of nucleotides differ from person to person. In the population, every person shows unusual sequences of 20- 100 base pairs, which are repeated several times. They are termed as Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTRs). The length of the regions having VNTRs
is different in each individual and hence is the key factor in DNA profiling.
Application of DNA fingerprinting
- In forensic science, DNA finger printing is used to solve problems of rape and some complicated murder cases.
- DNA finger printing is used to find out the biological father or mother or both, of the child, in case of disputed parentage.
- DNA finger printing is used in pedigree analysis in cats, dogs, horses and humans.
14. Briefly describe the following:
(a) Transcription
Answer :
It is the process to synthesize RNA from DNA template. During transcription, information of only one strand of DNA is copied into RNA. This strand of DNA acts as template. Enzyme RNA polymerase catalyses the formation of RNA transcript.
DNA transcription takes place in nucleus in eukaryotes whereas translation occurs in cytoplasm. DNA transfers information to m-RNA which then moves to ribosomes. Transcription occurs in the nucleus during G1 and G2 phases of cell cycle. DNA has promotor and terminator sites. Transcription starts at promotor site and stops at terminator site. Each transcribed segment of DNA is called transcription unit. It consists of
i. Promotor,
ii. The structural gene,
iii. A terminator.
Actually the process of transcription, in both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, involves three stages viz. Initiation, Elongation and Termination. The process of transcription is initiated when the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase and several initiation factors bind at the promoter region of the template. In prokaryotes, the enzyme recognizes the promotor by its sigma factor sub unit.
When RNA polymerase reaches the terminator signal on the DNA, it leaves DNA and fully formed mRNA (primary transcript) is released. As the mRNA grows, the transcribed region of DNA molecule becomes spirally coiled and attains (regains) double helical form.
(b) Polymorphism
Answer : Polymorphism involves one of two or more variants of a particular DNA sequence. Polymorphism promotes diversity and persists over many generations because no single form has an overall advantage or disadvantage over the others in terms of natural selection.
(c) Translation
Answer :
Translation is the mechanism in which codons of mRNA are translated and specific amino acids in a sequence form a polypeptide on ribosomes. All types of proteins are synthesised by the cell, within itself (i.e. intracellularly). Process of translation requires amino acids, mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, ATP, Mg++ ions, enzymes, elongation, translocation and release factors.
Ribosomes serve as site for protein synthesis. Each ribosome consists of large and small subunits. These subunits occur separately in cytoplasm. Only during protein synthesis, these two subunits get associated together due to Mg++ ions. A ribosome has one binding site for m-RNA and 3 binding sites for t-RNA. They are P site (peptidy t-RNA site), A site (aminoacyl– t-RNA site) and E site (exit site). Only first t- RNA- amino acid complex, directly enters P site of ribosome.
It involves three steps :
i. Initiation,
ii. Elongation,
iii. Termination

1. Initiation of Polypeptide chain :
a. Activation of amino acids is essential before translation initiates for which ATP is essential. Small subunit of ribosome binds (attaches) to the m-RNA at 5’ end. Initiator codon, AUG is present
on m-RNA which initiates the process of protein synthesis (translation). Initiator t- RNA binds with initiation codon (AUG) by its anticodon (UAC) through hydrogen bonds. It carries activated amino acid methionine (in Eukaryotes) or formyl methionine (in prokaryotes).
2. Elongations of polypeptide chain :
During this process, activated amino acids are added one by one to first amino acid (methionine). Amino acid is activated by utilising energy form ATP molecule. This amino acid binds with amino acid binding site of t-RNA- This results in formation of t-RNA- amino acid complex. Addition of Amino acid occurs in 3 Step cycle –
a. Condon recognition
b. Amino acid on the first initiator t-RNA at P-site and amino acid on t-RNA at A-site join by peptide bond.
c. Translocation- The t- RNA at A-site carrying a dipeptide at A-site moves to the P-site. This process is called translocation.
3. Termination and release of polypeptide:
At the end of m-RNA, there is a stop codon (UAA/ UAG/ UGA). It is exposed at the
A-site. It is not read and joined by anticodon of any t-RNA. The release factor binds to the stop codon, thereby terminating the translation process. The Polypeptide is now released in the
cytoplasm. Two subunits of Ribosome dissociate and last tRNA is set free in the cytoplasm. m-RNA also has some additional sequences that are not translated and are referred as untranslated regions (UTR). The UTRs are present at both 5’-end (before start codon) and at 3’-end (after stop codon). They are required for efficient translation process.bFinally mRNA is also released in the cytoplasm.
(d) Bioinformatics
Answer : Bioinformatics is combination biology, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has also been referred to as ‘computational biology’
The main components of bioinformatics are (1) the development of software tools and algorithms and (2) the analysis and interpretation of biological data by using a variety of software tools and particular algorithms.
Bioinformatics it is used to identify correlations between gene sequences and diseases, to predict protein structures from amino acid sequences, to aid in the design of novel drugs, and to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their DNA sequences (pharmacogenomics).
YB Study created with a vision to provide best education for students who try to crack NEET Entrance exam. YB Study offers Study Material in book Format, Online Test series, Live Classes, Recorded Classes, Video solution, Doubt Classes, Classroom Coaching to every students.
Why ybstudy.com Class 12 NCERT Solutions
- It is very Easy and Handy, simple to understand each question.
- Solutions developed by experts in the subject.
- It enhances the basic and conceptual knowledge of the students.
- This NCERT Solutions are also helpful for competitive exams like NEET, CET and other exams also.
- Easily available and easily accessible
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 PDF Download, Molecular Basis of Inheritance Class 12 NCERT Solutions PDF, Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Solutions, Molecular Basis of Inheritance exercise answers PDF, Molecular Basis of Inheritance Class 12 NCERT PDF, Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 question answer, Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 PDF Notes, Molecular Basis of Inheritance questions and answers.