Photosynthesis : Defination, Process, Functions and Types
Photosynthesis: Definition, Process, Functions and Types
Definition of Photosynthesis :
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process of forming food substances such as carbohydrates carried out by plants.
Or
Photosynthesis is the process of conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
Introduction to photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis occurs Especially in plants that contain leaf green substances or commonly referred to as chlorophyll.
- As we already know, plants are one of the types of living things. Unlike other living things, this plant can produce its own food through the process of photosynthesis.
- The reaction or stimulation of photosynthesis can occur because of several factors including chlorophyll and sunlight.
- As one type of living thing, plants or plants can indeed meet the requirements and characteristics of other living things.
- These characteristics or conditions such as breathing, moving, and breeding.
- But there is one thing that distinguishes it, between plants and other living things such as humans and animals.
- Namely with the ability of plants to make their own food.
- Plants are classified as autotrophic organisms that can make their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
- As described above, this photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that occurs by utilizing sunlight to be able to produce food that is needed by plants.
1. Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the utilization of sunlight energy carried out by leafy plants or bacteria to be able to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates. Meanwhile, the general definition of photosynthesis is the process of plants making their own food using light or sunlight.
2. Discovery of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process in which plants and some other living organisms get energy from a source. The source here is generally sunlight. Although this important process has been discovered since the beginning of time, all people are fully aware of its existence, and it was not discovered until the 1800s. Several different scientists for more than 200 years have contributed to the discovery of various natural phenomena regarding photosynthesis.
Here are some figures who discovered the photosynthesis process, including:
Jan Baptista
Photosynthesis was partially discovered in the 1600s by a scientist named Jan Baptista van Helmont. He is a chemist from Belgium as well as a physiologist and also a doctor. Helmont has been experimenting in 5 years involving willow trees which he planted in pots. By using the land. And also has been placed in a controlled environment. The willow tree is carefully watered for 5 years. At the end of his experiment, Helmont then came to the conclusion that tree growth was the result of nutrients that had been received from water. Helmont’s conclusion is the most accurate but his experiments also prove that water contributes to plant growth.
Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley is a scientist who also contributed to the discovery of photosynthesis. He was born in 1733 and later became a chemist, minister, natural philosopher, educator, and political theorist.
Experiments carried out by Joseph Priestley included placing a lit candle in a closed jar. Then, in 1774, the results of the experiment were published in his book entitled “Experiments and Observations of different types of Water, Volume I.” Although Priestley did not know at the time, the experiment proved that air contains oxygen.
Jan Ingenhousz
Jan Ingenhousz is another scientist who also contributed to the discovery of photosynthesis. He was a Dutch chemist, biologist, and physiologist who carried out important experiments in the late 1770s which proved that plants produce oxygen. Ingenhousz then places the submerged plants in the sun and then in the shade. Then he realized that the little bubbles had been produced by plants when they were in the sun. By the time they have been transferred to color bubbles that are no longer produced by this plant. Ingenhousz then came to the conclusion that plants could use light to produce oxygen.
Jean Senebier
In 1796, Jean Senebier, a Swiss botanist, priest, and naturalist, stated that plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen by using sunlight. In the early 1800s Nicolas-Theodore de Saussure also provided information that while plants need carbon dioxide, the increase in plant mass that grows is not the result of carbon dioxide alone but also the result of water absorption.
Julius Robert Mayer
In the 1840s, Julius Robert Mayer, a German doctor, and physicist said that energy could not be created or destroyed. This is known as the first law of thermodynamics. He proposed that plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Julius Sachs
In the years 1862-1864 Julius Sachs conducted research on how starch is produced under the influence of light and what it has to do with chlorophyll. That ultimately led him to write a general equation for photosynthesis (6CO2 + 6H2O2 → (with light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 /).
3. Functions of Photosynthesis
Here are some of the functions or objectives of plants that carry out photosynthesis, including the following:
1. Producing Glucose
- The first function of photosynthesis is to make a food substance in the form of glucose, where this glucose will then be used as a basic fuel and then processed again until it becomes another food substance.
- The results of the processed process are in the form of protein and fat contained in plants.
- The processed substances will then also provide benefits for humans and animals to be consumed.
2. Produces O2 and Reduces CO2
- The process of photosynthesis that requires carbon dioxide can actually help us in reducing levels of carbon dioxide found in the environment.
- And as we already know as the result of the photosynthesis process one of the most important is oxygen.
- Oxygen is the primary need of humans and other living things, without oxygen or clean air, humans and other living things will not survive.
3. Producing Coal
- Photosynthesis carried out by plants when the plants were still alive turned out to be able to make the remains of plants buried in the soil for years can become coal.
- This is also very important in today’s life, given that coal has many different functions and benefits.
- So, we should try to continue to preserve plants in the environment around us.
4. Photosynthesis Process in Plants
- Plants have autotrophic properties. Autotroph itself means that it can synthesize food directly from inorganic compounds.
- Plants can use carbon dioxide and water to produce sugar and oxygen that are already needed as food.
- The energy used to carry out this process comes from the process of photosynthesis.
- The following are photosynthetic reactions in producing glucose, namely:
- Glucose can be used in the formation of other organic compounds such as cellulose and can also be used as fuel.
- The process takes place through cellular respiration that takes place both in animals and in plants.
- In general, the reactions that take place in cellular respiration are the opposite of the equation above.
- In respiration, sugar (glucose) and other compounds will react with oxygen in terms of producing carbon dioxide, water, and also chemical energy.
- Plants will then capture light by using a pigment called chlorophyll. That pigment will later give the plant a green color.
- Chlorophyll is in organelles called chloroplasts. This chlorophyll serves as a light absorber that will later be used in the process of photosynthesis.
- Although all parts of the plant body that have a green color contain chloroplasts, most of the majority of energy is produced in the leaves.
- Inside the leaves, there are various layers of cells called mesophiles which contain half a million chloroplasts in every square millimeter.
- The light is then carried through the epidermal layer without color or transparency, to the mesophyll, where most of the photosynthesis process takes place.
- The surface of the leaves has generally been coated by cuticles derived from wax which are waterproof to prevent the absorption of sunlight or excessive evaporation of water.
5. Photosynthesis in Algae and Bacteria
- Algae consist of several multicellular algae such as algae to microscopic algae that consist of only one cell.
- Although algae do not have a complex structure in terrestrial plants, photosynthesis in both occurs in the same way.
- It’s just that, because the algae have various types of pigments in their chloroplasts, the length of the light waves that they will absorb will also be more varied.
- All algae can produce oxygen which most have autotrophic properties.
- Only a small proportion are heterotrophic, which means that they depend on the material that can be produced by other organisms.
- Plants need sunlight, water, and also air to make their own food. Every day, leaf green substances in the leaves of plants can absorb sunlight.
- Plants use sunlight which will later be converted into carbon dioxide from the air, and water from the land that will be converted into foods that already contain sugar.
- Before the process of photosynthesis takes place, only green plants can later do the process because green plants have chlorophyll.
- Not only that but photosynthesis can also be done during the day when there is sunlight.
- In addition to sunlight, plants also need water and carbon dioxide to carry out the chemical reaction of photosynthesis.
- Plants can get carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air which will later enter the leaves of plants through the stomata or leaf mouth.
- As for water (H2O) can only be obtained through plant roots which will be passed on to the leaves through plant stems.
- When the sun’s rays fall to the surface of the leaves, then chlorophyll captures the energy of the sun’s rays.
- The captured light will then pass through the transparent layer of the epidermis. And then continue back to the mesophyll. In this mesophyll most of the process of photosynthesis takes place.
- The energy is then used to convert water into sugar or glucose (C6H12O6) and into oxygen (O2). After that, the results of the photosynthesis process will be able to become food for plants.
- While the oxygen produced will then be released by plants through stomata. This oxygen is then released into the air to be breathed by all living things such as humans and animals.
6. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
4 factors can affect the photosynthesis process needed by plants to be able to carry out the process of photosynthesis. Among other things, namely chlorophyll, sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. In the following, we will give a more detailed explanation of each component of photosynthesis and their understanding. Check out below:
1. Chlorophyll
- To be able to carry out the process of photosynthesis, the plant must have chlorophyll or what we commonly know as leaf green matter.
- The definition of chlorophyll according to KBBI is a plant greening agent (especially on leaves) which is the most important in the process of photosynthesis.
- Organisms or plants that do not have chlorophyll cannot carry out the process of photosynthesis. Plants that have chlorophyll have autotrophic properties.
- Namely, organisms that can produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis.
2. Sunlight
- One of the most important photosynthetic factors is the presence of sunlight.
- If there is no sunlight, the green plants will not be able to carry out this photosynthesis process.
- That would be the process of photosynthesis which can only take place during the daytime when the sun is shining.
- The intensity of sunlight will greatly have a large influence on the occurrence of photosynthesis.
- The higher the intensity of light from the sun, the more energy will be produced. So that the photosynthesis process that takes place will be even faster and vice versa.
3. Water (H2O)
- In carrying out photosynthetic reactions, this plant will also need water or H2O as one of the factors or ingredients.
- If there is no water, the photosynthesis process can be inhibited. Water can only be obtained by roots that absorb water through the soil.
- Lack of water during drought can cause stomata in plants to be closed. This can cause the absorption of carbon dioxide will decrease.
- And can also inhibit the process of photosynthesis. Therefore, water is needed in the process of photosynthesis.
4. Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Not only water, but plants also need carbon dioxide or CO2 to be able to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide will be an important component when the process of photosynthesis takes place. Plants can get carbon dioxide in free air through stomata.
- And including the results of the rest of the respiration carried out by humans or animals.
- The more carbon dioxide in the air, the more amount of carbon dioxide material that can be used by plants to carry out a process of photosynthesis.
5. Temperature
- The higher the temperature, the faster the process of photosynthesis. Because it is a chemical process, the temperature of all actions also increases.
- When the temperature is higher than 40 ° C, the rate of the process slows down because the chemical processes occurring at this temperature are sensitive and perish at high temperatures.
- If the temperature is cold then the process is slow. The temperature has a great effect on the enzymes of action.
6. Photosynthesis Reaction
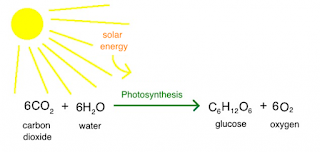
In general, plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose or sugar and oxygen needed as food in a process of photosynthesis with the help of sunlight.
The following are the photosynthetic reaction equations.
6H2O + 6CO2 + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Information:
H2O = water
CO2 = carbon dioxide
C6H12O6 = sugar or glucose
O2 = oxygen
7. Reactions of Photosynthesis
In a process or reaction in photosynthetic processes, there are two kinds, namely reactions to light and dark.
The following is a reaction from photosynthesis:
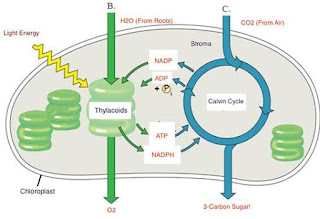
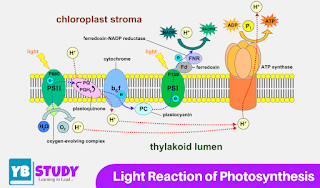
7.1 Light reactions
- Light reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane that is on the grana.
- Grana is a structure formed from thylakoid membranes formed in the stroma, which is one of the chambers in the chloroplast.
- In the grand, there is chlorophyll as a pigment that plays a role in the ongoing process of photosynthesis.
- The light reaction is called photolysis because there is a process of absorption of light energy and the breakdown of water molecules that turn into oxygen and hydrogen.
Acyclic-light phosphorylation: It involves the flow of electrons from water molecules to light system II, followed by the light mechanism I and finally to NADP, which is reduced to NADPH2. Because the flow of electrons in it is unidirectional, it is called acyclic light phosphorylation.
Cyclic Light phosphorylation: In some circumstances when acyclic light phosphorylation stops, cyclic light phosphorylation occurs and occurs only in the light system I (PSI). In this process, the electrons return to the oxidized P700 reaction center. Thus low energy level transfer of electrons leads to ATP formation and is called cyclic light phosphorylation.
7.2 Dark reactions
- Dark reactions occur in the stroma. This reaction will form sugar from the basic ingredients of CO2 obtained from the air and the energy obtained from the light reaction.
- It no longer requires sunlight, but this reaction cannot occur if there has not been a light cycle. Because the energy used comes from light reactions.
- In the dark reaction, there are two kinds of cycles, namely the Calin-Benson cycle and the Hatch-Slack cycle.
- In the Calin-Benson cycle, the plant will later produce compounds with the number of three carbon atoms, namely 3-phosphoglycerate compounds.
- This cycle is greatly helped by the presence of the rubisco enzyme.
- While in the Hatch-Slack cycle, plants will produce compounds with a carbon atom of four.
- The enzyme that plays a role in this second cycle is phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase.
- The final product of the dark cycle is obtained glucose which will later be used by plants for their activities or stored as energy or food reserves.
The dark reaction involved 2 steps
1. C3 or Calvin cycle
2. C4 or HSK pathway
C3 cycle Calvin
Cycle In this cycle, the atmosphere is initially taken up by atmospheric carbon sugars (ribulose by phosphate), and two molecules of the 3-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, are formed. This three-carbon molecule is the first permanent product of this path, so it is called a cycle. The process of manufacturing is called carboxylation. This reaction is induced by the enzyme ribulose biphosphate phosphate carboxylase. This enzyme is probably the most commonly found protein on Earth.
In the second phase, PGA is reduced to a 3-carbon carbohydrate called trios phosphate with the help of NADPH2 and ATP. (NADPH2 and ATP are obtained in light reaction) A. Most of these molecules are released from the C3 cycle and they are used in the synthesis of other carbohydrates such as glucose and sucrose. To complete the cycle, the initial 5 carbon receptor molecules are regenerated by the molecule from triose phosphate and the cycle starts again.
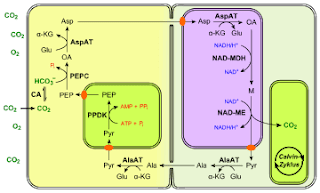
C4 cycle (hatch and slack cycle)
The C4 cycle seems to be an adaptation for plants that grow in dry and hot environments. Such plants can do photosynthesis even when they have very small amounts of carbon dioxide and partial closure of stomata pores.
Such plants can grow rapidly even in small quantities of water, high temperature, and high light – sugarcane, maize, sorghum are some such plants.
- Photorespiration (oxidation of RUBP in the presence of oxygen) is absent in these plants. Therefore, the rate of photosynthesis in them is high.
- The leaves of C4 plants have a special type of structure called Crane morphology. The characteristics of the leaves of C4 plants are as follows
- The leaves have a layer of messenger cells on each side of each vascular bundle called the bundle mask, which is also called the cartridge morphology.
- There are two types of green turtles (two-dimensional green turtles) in leaves.
- Leaf mesophyll cells have relatively small green leaves, they also have well-developed granules, but do not contain starch.
- The cysts within the cells of the bundle cover are relatively large in size and do not contain granules but contain numerous starches.
- The primary receptors of CO2 in C4 plants are 3 carbon atoms, phosphoenol pyruvic acid, or PEP. This phosphoenol pyruvate combines with CO2 in the presence of a carboxylase enzyme to form a four-carbonic acid, oxaloacetic acid. This stabilization of CO2 occurs in the cytoplasm of the mesophyll cell. OAA is the first four carbon-containing products of this cycle, hence it is also called the C4 path.
- The OAA leads from the mesophyll cell to the epithelium of the bundle clade where it releases CO2. In these cells, C3 cycles in cells and CO2 instantly binds to RUBP and forms sugars by the C2 cycle.
- Thus the C4 cycle of non-ferrous reaction proceeds and CO2 immediately binds to RUBP to form sugars by the C3 cycle.
- Thus, there are two carboxylase enzymes in the C4 cycle of non-ferrous reaction. 1. PEPCase which is found in mesophyll cells and Rubisco which is found in bundle clad cells.
Types of Photosynthesis
1. Oxygenic photosynthesis
- Oxygenic photosynthesis is the most common process seen in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
- During the process of oxygenic photosynthesis, the light will transfer the energy of electrons from water (H2O) to carbon dioxide (CO2) and eventually will produce carbohydrates.
- In this transfer process, CO2 that is “reduced,” or receives electrons, and also water will become “oxidized,” or lose electrons.
- So that in the end, oxygen will be produced together with carbohydrates
- The function of oxygenic photosynthesis is to balance respiration, needed in carbon dioxide which will later be produced by all breathing organisms and will be given back in the form of oxygen to free air.
- In his 1998 article, “An Introduction to Photosynthesis and Its Applications,” Wim Vermaas who is a professor from Arizona State University suspected that “without oxygenic photosynthesis, oxygen in the air would be depleted in several thousand years.”
2. Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
- On the other hand, anoxygenic photosynthesis will use donor electrons in addition to water. This process generally takes place in bacteria such as purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria.
- Anoxygenic photosynthesis will not produce oxygen, so David Baum who is a botany professor from the University of Wisconsin Madison said:
- What will be produced will depend on the electron donor.
- For example, some bacteria use odorous egg gas, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur, to produce solids as a by-product.
8. Photosynthesis Chemical Reaction
- In a photosynthetic reaction, energy from the sun will then be converted into chemical energy.
- The chemical energy will be stored in the form of glucose (sugar).
- Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight will be used to produce glucose, oxygen, and water.
- The chemical equation for this photosynthesis process is:
- 6CO2 + 12H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
- If we look at the reaction above, then 6 molecules of carbon dioxide (6CO2) and 12 molecules of water (12H2O) are consumed in the process.
- As for glucose (C6H12O6), six molecules of oxygen (6O2), and also six molecules of water (6H2O) are produced.
- This equation can also be simplified as:
- 6CO2 + 12H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O.
8.1 Types of Chemical Reactions
As for the types themselves, these chemical reactions can be grouped according to their similarities. To be able to facilitate the learning process.
One of the systems used to classify them is based on how atoms can be rearranged in chemical reactions. Following full review …
A. Merging reaction
- This group can take place if between the two substances or can act more and then form other substances
- For example, as in hydrogen and also oxygen that reacts and will later produce water, which is 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
B. Decomposition reaction
- While this second group can occur if one substance is broken down into one substance or it can be more
- For example: 2NH3 → N2 + 3H2
C. Replacement reactions
- The latter group can take place when one atom replaces the other atoms contained in one compound.
- For example: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2. In this reaction Mg replaces Cl.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis in green plants is a very important activity for plants and other living beings. In this process, the plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy and complex carbon compounds become carbohydrates from simple substances like CO2 water.
It is only through these carbohydrates that humans and living beings get food. In this way, plants make food for the whole animal world by the process of photosynthesis. Various crops are grown to obtain carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, etc., and all these substances are produced by photosynthesis.
Green trees take carbon dioxide in the process of photosynthesis and remove oxygen, thus purifying the atmosphere. Oxygen is essential for all animals to breathe. This action is also very important for the protection of the environment. Photosynthesis is also very important for fisheries.
When the process of photosynthesis slows down, the amount of carbon dioxide in water increases. It is exceeding 5 cc per liter is harmful to fisheries. Photosynthesis is also helpful in making biofuels. Through this, plants also produce biofuels through solar energy. This biofuel goes through various processes and produces a variety of energy sources.
Based on appropriate facts, it is concluded that the photosynthesis process is very important for life on earth. Sunlight, water, and plants work together to maintain life on earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where would photosynthesis take place?
Answer: The green parts of photosynthesis mainly occur through leaves, sometimes also green stems and flower buds. Specialized cells of the leaves, called mesophylls, are found in their green leaves. This green circle is the real center of photosynthesis.
Thus a brief review this time that we can convey. Hopefully, the above review can be made as your learning material.