Hematopoiesis : Basics of Hematopoiesis, Sites, Process and types
Hematopoiesis : What is Hematopoiesis, Definition, Site, Process, and types :
What is Hematopoiesis ?
- Hematopoiesis (or hemopoiesis) is defined as it is the biological process by which Red blood cells, White blood cells, and platelets are formed.
- It covers all phenomena related to the origin, multiplication, and maturation of primordial cells or precursors of blood cells.
- The blood is made up of 3 different kinds of cells : erythrocytes, white blood cells, and platelets. These three cell lines, despite being distinct from each other, come from a single mother cell, called pluripotent, totipotent, or stem cell.
- Generally, hematopoiesis occurs in the firstly in the yolk sack, followed by the liver, and lastly in the bone marrow.
- Hematopoiesis occurs in the specific type of stem cell known as Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) which give rise to other different types of blood cells.
- Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are present in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and it has the unique potential to give rise to the other different mature blood cell types and tissues.
What are hematopoietic stem cells?
- Generally, Stem cells are primitive cells that have the potential for self-replication and multidirectional differentiation into other cell types. They are the originator cells that produce progenitor cells that form the various tissues and organs of the human body.
- Hematopoietic stem cells are the cells of origin of all Blood cells red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Some studies show that hematopoietic stem cells can also differentiate into cells of various tissues and organs across the system, so they are multifunctional stem cells.
- Adult hematopoietic stem cells mainly exist in the red bone marrow and can migrate into the peripheral blood circulation through the bloodstream.
- Hematopoietic stem cells can also be found in the liver and spleen.
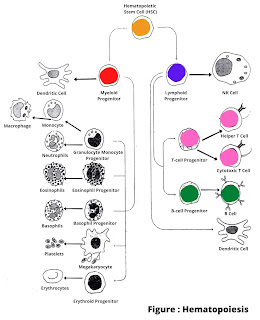
There are three main types of hematopoietic stem cells and each type of hematopoietic cell produces a different group of blood cells. All blood cells originate from a single type of Stem cell are called Hematopoietic stem cells.
- Erythroid Progenitor Stem cells : This is the lineage that produces Erythrocytes also known as red blood cells. (RBC). Erythropoiesis begins with the differentiation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) into the most primitive erythroid progenitors. The developing red blood cells are called erythroblasts.
- Granulocytes Progenitor Stem Cells: This lineage produces white blood cells, such as neutrophils. Immature granulocytes are called myeloblasts.
- Megakaryocytes Progenitor Stem Cells: This lineage produces platelets. Platelets come from large cells called megakaryocytes.
Site of Hematopoiesis :
- Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) are specialized stem cells that produce all types of blood cells. Stem cells can differentiate into other cell types. generally, stem cells are self-renewing, maintain their own population level by the process of cell division.
- In humans, the process of hematopoiesis, or the formation and development of RBC, WBC, and Platelets, begins in the first week of development in the embryonic yolk sac. In the Yolk sac stem cells differentiated into primitive erythroid cells that contain embryonic hemoglobin.
- In the third month of gestation, hematopoietic stem cells migrated from the yolk sac to the liver and spleen and now the hematopoiesis process occurs in these two organs from the third to seventh month of gestation.
- After birth, these hematopoietic stem cells migrate from these two organs to the bone marrow where hematopoiesis occurs. After birth, no hematopoiesis occurs in the liver and spleen.
Process of Hematopoiesis :
- The process of Hematopoiesis occurs in various organs like embryonic yolk sac, liver, spleen, kidney, lymph node, bone marrow, and so on.
- Hematopoiesis begins in the third week of the gestation. At this stage, there is no organ formation. An embryonic tissue called the yolk sac is responsible for hematopoiesis.
- At the 6th week of the human embryo, human organs are formed and the liver continues to make blood.
- In the third month of the human embryo, the spleen is the main hematopoietic organ.
- After the fourth month of the human embryo, the bone marrow begins to make blood, which is the most important hematopoietic tissue in the human body.
- After birth hematopoiesis in the liver and spleen has stopped and the bone marrow takes full responsibility for hematopoiesis.
- Blood cells include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, etc.
- They each perform their duties, but they all come from the same type of pluripotent stem cells known as hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). The proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of pluripotent stem cells form various end blood cells flowing in blood vessels.
- Early in hematopoiesis, a multipotent stem cell differentiated into two pathways, giving rise to either a lymphoid progenitor cell or a myeloid progenitor cell. Progenitor cells have lost the capacity for self-renewal and are committed to a particular cell lineage.
- Lymphoid progenitor cells give rise to B, T, and NK (natural killer) cells.
- Myeloid stem cells generate progenitors of red blood cells (erythrocytes), many of the various white blood cells (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, mast cells, dendritic cells), and platelet-generating cells called megakaryocytes.
What kinds of Cells are produced by Hematopoiesis?
- Monocytes: are also responsible for infection control; they are important in immune processes and in removing dead tissues or cells. They also exist in the various organs, where they are called “macrophages”.
- Neutrophils: are the most numerous white blood cells and the most important in controlling infections.
- Eosinophils: important in controlling parasite infections; they also increase in allergies and with some medications.
- Basophils: involved in allergic reactions, release histamine.
- Lymphocytes: They are responsible for our immunity and for other processes, such as autoimmune diseases (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc) and for the rejection of transplants. There are several types of lymphocytes B -lymphocytes – differentiate into plasma cells, which are antibody-producing cells. Antibodies are a particular type of protein – immunoglobulins. T lymphocytes – stimulate the production of B lymphocytes and produce several cytokines. NK (natural killer) cells – they destroy tumor cells and also act on immunity.