What is banking of road? Angle of banking and expression.
Banking of Road: Definition, Expression, and Importance:
Banking of road: For the safety of a vehicle moving along a curved road at high speed, the road surface is kept inclined horizontally so that the outer edge of the road is at a higher level than the inner edge. This construction or arrangement of the road is called the banking of the road.
The angle of banking ( θ ): The angle made by a banked road surface with horizontally is called as the angle of banking.
Expression for banking of road ( θ ) :
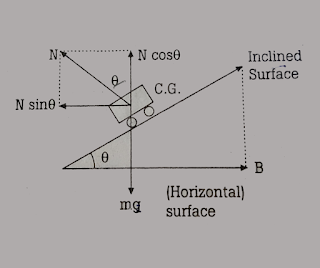
1) Consider a vehicle of mass ‘m’ moving with speed v, along a banked road. Let ‘r’ be the radius of curvature and θ be the angle of banking.
2) The forces acting on the vehicle when the vehicle is moving on a banked road are__
- The weight mg acts in a vertically downward direction.
- The normal reaction N is perpendicular to the banked road.
3) The normal reaction N can be resolved into two components,
- N cosθ in a vertically upward direction.
- N sinθ along the horizontal direction.
- the angle of banking (θ)
- the radius of the curved road (r)
- acceleration due to gravity at that place (g).
Necessity banking of the road:
(Need for banking of road)
1) When a vehicle moves along a horizontal curved road, necessary centripetal force is supplied by the force of friction between the wheels of the vehicle and the surface of the road.
2 Frictional force is not enough and reliable every time as it changes when the road becomes Oily or wet in the rainy season.
3) To increase the C.PE. the road should be made rough. But it will cause wear and tear on the tires of the wheel.
4) Thus, due to a lack of centripetal force vehicle tends to skid.
5) When the road is banked, the horizontal component of the normal reaction provides the Necessary centripetal force required for the circular motion of the vehicle.
6) To Provide the necessary centripetal force at the curved road banking of the road is necessary.
MCQs on Banking of road
1. While taking turns on a curved road, a cyclist has to bend through a certain angle. This is done______
(a) to reduce his speed
(b) to decrease the friction between the tires and the road
(c)To get the necessary centripetal force
(d) to reduce his weight
Answer: C
2. An airplane is taking a turn in a horizontal plane. While
taking the turn_____
(a) it remains horizontal
(b) it inclines outwards
(c) it inclines inward
(d) it makes its wings vertical
Answer: C
3. When a car takes a turn on a horizontal road, the centripetal force is provided by the______
(a) weight of the car
(b) the normal reaction of the road
(c) the frictional force between the surface of the road and the tires of the car
(d) centrifugal force
Answer: C
4. While taking a sharp turn, a car moving on a horizontal road, may be thrown out of the road. This happens_______
(a) due to frictional force between the tires and the road
(b) due to gravitational force
(c) due to lack of sufficient centripetal force
(d) due to the reaction of the ground.
Answer: C
5. When a car takes a circular turn on a banked road, the Centripetal force is provided by______
(a) gravitational force
(b) frictional force
(c) If a horizontal component of normal reaction
(d) the vertical component of normal reaction.
Answer: C
6. A cyclist moves on a circular track with a radius of 100m. If the coefficient of friction is 0.2, then the maximum velocity with which the cyclist can take the turn with leaning inward Is_______
(a) 140 m/s
(b) 14 m/s
(c) 1.4 m/s
(d) 4.9 m/s
Answer: B
7. A curved road having a radius of curvature of 30m is banked at the correct angle. If the speed of the car is to be doubled, then the radius of curvature of the road should be__________
(a) 62 m
(b) 120 m
(c) 90 m
(d) 15 mn
Answer: B
8. A vehicle sometimes overturns while taking a turn. When it overturns______
(a) The outer wheels leave the ground first
(b) The inner wheels leave the ground first
(c) All wheels leave the ground simultaneously
(d) either the inner wheels or the outer wheels leave the ground first. It depends upon the total weight of the vehicle
Answer: B
9. A car is moving on a circular horizontal track with a radius of 10m with a constant speed of 10 m/s. A plumb line is suspended from the roof of the car by a light rod of length 1m. What is the angle made by the rod with the track? (g = 10 m/s)
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 0°
Answer: B
10. On a banked road, the centripetal force is provided by________
(a) the frictional force
(b) weight of the car.
(c) the vertical component of the (resultant) normal reaction
Answer: B