Class 12 chemistry chapter 14 Biomolecules solutions
Maharashtra state Chemistry Textbook Solutions for Class 12 are very important and crusial that helps the students in understanding the complex topics and helps them in the preparation of class 12 board examination as well as verious compititive entrance examinations also. Studying the answers to the questions in the Chemistry textbook will check your understanding of a particular topic and helps you determine your strengths and weaknesses.
Class 12 chemistry textbook Solutions for Class 12, Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules maharashtra tate board are provided here with simple step-by-step detailed explanations. These solutions for Biomolecules are very popular among Class 12 students for chemistry chapter 14 Biomolecules Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the chemistry textbook Solutions Book of Class 12 chemistry Chapter 14 are provided here for you for free. You will also love the experience on ybstudy class 12 Solutions. All chemistry textbook Solutions. Solutions for class 12, These chemistry textbook solutions are prepared by Chemistry experts and are 100% accurate.
1. Select the most correct choice.
i. CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4CH2OH is an
example of
a. Aldohexose
b. Aldoheptose
c. Ketotetrose
d. Ketoheptose
ii. Open chain formula of glucose does not contain
a. Formyl group
b. Anomeric hydroxyl group
c. Primary hydroxyl group
d. Secondary hydroxyl group
iii. Which of the following does not apply
to CH2NH2- COOH
a. Neutral amino acid
b. L – amino acid
c. Exists as zwitter ion
d. Natural amino acid
iv. Tryptophan is called essential amino
acid because
a. It contains aromatic nucleus.
b. It is present in all the human
proteins.
c. It cannot be synthesised by human
body.
d. It is essential constituent of
enzymes.
v. A disulfide link gives rise to the following structure of protein.
a. Primary
b. Secondary
c. Tertiary
d. Quaternary
vi. RNA has
a. A – U base pairing
b. P-S-P-S backbone
c. double helix
d. G – C base pairing
2. Give scientific reasons :
i. The disaccharide sucrose gives negative Tollens test while the disaccharide maltose gives positive Tollens test.
Answer :
ii. On complete hydrolysis DNA gives
equimolar quantities of adenine and
thymine.
Answer : A DNA molecule is double-stranded in which the pairing of bases occurs. Adenine always pairs with thymine, while cytosine always pairs with guanine. Therefore, on hydrolysis of DNA, the quantity of adenine produced is equal to that of thymine and similarly, the quantity of cytosine is equal to that of guanine.
iii. α – Amino acids have high melting points compared to the corresponding
amines or carboxylic acids of comparable molecular mass.
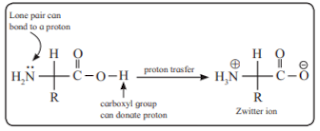
Answer : Amino acids have two functional groups −NH2 and −COOH. Hence the amino acids exist as a dipolar ion (or) zwitterion. As a result, strong electrostatic forces exist between zwitterions. Hence amino acids have high melting points than the corresponding halo-acids.
iv. Hydrolysis of sucrose is called
inversion.
Answer : Sucrose (C12H22O11) is
dextrorotatory (+66.50). On hydrolysis with
dilute acid or an enzyme called invertase
sucrose gives equimolar mixture of D-(+)
glucose and D-(-) fructose.
Since the laevoratotion of fructose (-92.40)
is larger than the dextrorotation of glucose
(+52.70), the hydrolysis product has net
laevorotation. Hence hydrolysis of sucrose
is also called inversion of sucrose, and the
product is called invert sugar.
v. On boiling egg albumin becomes
opaque white.
Answer : As an egg cooks, the heat causes the bonds within the proteins to break, a process called denaturation. As these proteins chains unfold and entangle with other proteins, new bonds form between these amino acids and the amino acids of neighboring proteins, causing the texture to change and it turns white.
3. Answer the following
i. Some of the following statements
apply to DNA only, some to RNA
only and some to both. Lable them
accordingly.
a. The polynucleotide is double
stranded. (……… )
Answer : DNA
b. The polynucleotide contains uracil.
(……… )
Answer : RNA
c. The polynucleotide contains D-ribose (……… ).
Answer : DNA
d. The polynucleotide contains Guanine (……… ).
Answer : Both DNA & RNA
ii. Write the sequence of the
complementary strand for the
following segments of a DNA
molecule.
a. 5′ – CGTTTAAG – 3′
Answer :
5′ – CGTTTAAG – 3′
3′ – GCAAATTG – 3′
b. 5′ -CCGGTTAATACGGC – 3′
Answer :
5′ -CCGGTTAATACGGC – 3′
3′ – GGCCAATTA+GCCG – 5′
iii. Write the names and schematic representations of all the possible
dipeptides formed from alanine,
glycine and tyrosine.
Answer :
iv. Give two evidences for presence of
formyl group in glucose.
Answer : To prove the presence of −CHO group: When glucose reacts with hydroxylamine, oxime is formed and cyanohydrins are formed on the addition of hydrogen cyanide to it. This reaction can confirm the presence of carbonyl group in glucose.
4. Draw a neat diagram for the following:
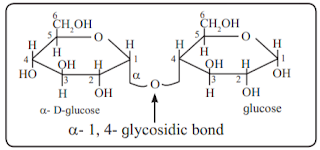
i. Haworth formula of glucopyranose
ii. Zwitter ion
iii. Haworth formula of maltose
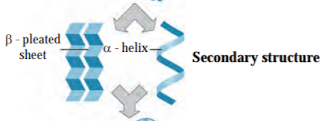
iv. Secondary structure of protein
vii. One purine base from nucleic acid
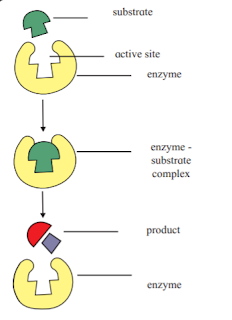
viii. Enzyme catalysis