Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Life Processes In Living Organisms Part 1 Exercise
Life processes in living organisms part -1 chapter 2 Textbook Solutions :
Students can refer to the following Life processes in living organisms part -1 chapter 2 textbook solutions for class 10 Science provided below based on the latest curriculum and examination pattern issued by Maharashtra state board. Our subject experts have prepared these questions and answers for class 10 students. which covers all topics from your textbook so that students can assess themselves on all important topics and thoroughly prepare for their board exams.
We have provided below Life processes in living organisms part -1 chapter 2 class 10 notes Science with answers which will help the students to go through the entire syllabus and and practice textbook questions and answers provided here with solutions. You can download in Pdf Format and score high in your board exam you should go thorough all Life processes in living organisms part -1 chapter 2 Class 10 solutions provided below so that you are able to get more marks in your exams
Important points to Remember about Life Processes in living organisms:
- Various organ-systems are continuously performing their functions in human body. Along with the various systems like digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory and control systems, different external and internal organs are performing their functions independently but through a complete co-ordination.
- This overall system is in action in more or less same way in all the organisms. Those are in need of continuous source of energy for this purpose.
- Carbohydrates, fats and lipids are the main sources of this energy and it is harvested by the mitochondria present in each cell.
- It is not like that only foodstuff is sufficient for energy production but oxygen is also necessary. All these i.e. food stuffs and oxygen are transported up to the cell via circulatory system.
- Besides, it is coordinated by the control system of the body. i.e. each life process contributes in its own way in the process of energy production.
- Functioning of all these life processes also requires the energy.
- Human and other animals consume the fruits and vegetables. Plants are autotrophs.
- They prepare their own food. They utilize some of the food for themselves whereas remaining is stored in various parts like fruits, leaves, stem, roots, etc.
- We consume all these various plant materials and obtain different nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.
- We obtain the carbohydrates from milk, fruits, jaggary, cane sugar, vegetables, potatoes, sweet potatoes, sweet meats and cereals like wheat, maize, ragi, jowar, millet, rice, etc.
Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Life Processes In Living Organisms Part 1 Exercise with Answers :
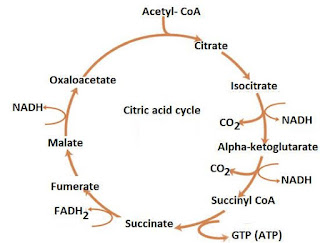
| Glycolysis | TCA cycle |
|---|---|
| Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm | TCA cycle occurs in the matrix of mitochondria |
| Glycolysis can take place in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration | TCA cycle take place during aerobic respiration |
| Glycolysis occurs as linear sequence | TCA cycle Occurs as a cyclic sequence |
| Oxygen is not Necessary for glycolysis | Oxygen is Necessary for TCA cycle |
| Substrates is glucose | Substrates is acetyl-CoA |
| It produces pyruvic acid, NADH and ATP | It produces oxaloacetic acid, NADH, FADH2, ATP and CO2 |
| It’s generates 2 ATP molecules from 1 glucose molecules | It generates 2 GTP / ATP molecules from 2 acetyl – CoA molecules |
| CO2 is not produced during glycolysis | CO2 produced in TCA cycle |
| It occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes | It occurs only in eukaryotes |
| Glycolysis also called as EMP pathway | TCA cycle also called as Krebs cycle |
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|
| Mitosis discovered by Walther Flemming | Meiosis discovered by Oscar hertwig |
| Mitosis occurs in all organisms, except viruses | Meiosis occurs only in animals , plant and fungi |
| Mitosis create body / somatic cells | Meiosis crests germ / sex cells |
| Mitosis involves one cell division | Meiosis involves two successive cell division |
| Mitosis perform general growth repairs, Cell reproduction. | Meiosis perform genetic diversity through sexual reproduction |
| Mitosis is the process where the division of cells occurs by asexual reproduction | Meiosis is the process Where the division of cells occurs by sexual reproduction |
| In mitosis number of chromosomes remain the same | In meiosis number of chromosomes reduce by half |
| In mitosis Tetrad formation does not occur. | In meiosis tetrad formation Occurs and it’s Consists of two sets of sister chromatids |
| In mitosis sister chromatids separate | In meiosis sister chromatids do not separate |
| In mitosis length of prophase is short | In meiosis length of prophase I is long and it’s consist five stages are leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, Diplotene and diakinesis. |
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
|---|---|
| Oxygen is present when this form of respiration take place | Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration take place |
| It can be found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria | It can be found only in the cytoplasm |
| Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water | Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide, ethyl alcohol and energy |
| It involves the exchange of gases between the organisms and outside environment | In anaerobic respiration exchange of gases is absent |
| In aerobic respiration high amount of energy is produced | In anaerobic respiration less amount of energy is produced |
| A net gain 36 molecules of ATP occurs. | A net gain of only 2 molecules of ATP occurs |
| All higher organisms such as mammals have this type of respiration | Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast are this type of respiration . |
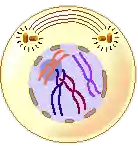
- In prophase, condensation of basically thin thread-like chromosomes starts.
- Due to this, they become short and thick and they start to appear along with their pairs of sister chromatids.
- Centrioles duplicate and each centriole moves to opposite poles of the cells.
- Nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
- Nuclear membrane completely disappears in metaphase.
- Chromosomes complete their condensation and become clearly visible along with their sister chromatids.
- All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane (central plane) of the cell. Special type of flexible protein fibers (spindle fibers) are formed between centromere of each chromosome and both centrioles.
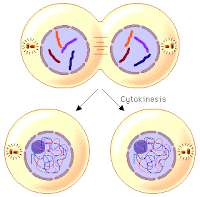
- In anaphase, centromeres split and thereby sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and they are pulled apart in opposite directions with the help of spindle fibers.
- Separated sister chromatids are called as daughter chromosomes.
- Chromosomes being pulled appear like bunch of bananas.
- In this way, each set of chromosomes reach at two opposite poles of the cell.
- The chromosomes which have reached at opposite poles of the cell now start to decondense due to which they again become thread-like thin and invisible.
- Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes reached at poles. Thus, two daughter nuclei are formed in a cell.
- Nucleolus also appears in each daughter nucleus. Spindle fibers completely disappear.
Cytokinesis :The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis and two new cells are formed which are called as daughter cells. In this process, a notch is formed at the equatorial
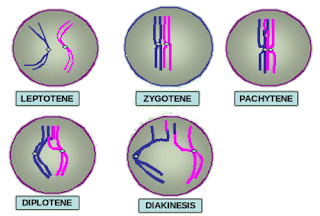
1. Leptotene : Condensation makes chromosomes become distinct and compact.
2. Zygotene : Homologous chromosomes start pairing together by a process called synapsis to form a complex structure called synaptonemal complex. Two synapsed homologous chromosomes form a complex called bivalent or tetrad.
3. Pachytene : Longest phase of prophase I Recombination nodules appear in this stage at the sites where crossing over has to take place between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
4. Diplotene : Synaptonemal complex dissolves and recombinants separate from each other except at crossover sites to form X-shaped structure called chiasmata.
5. Diakinesis : Chiasmata terminalises and chromosomes condense. Meiotic spindle assembles and nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear.
- Nutrition is where an element takes food and uses it for energy. It is an essential organic cycle that encourages living creatures to acquire their energy from different sources.
- Transportation or transportation framework in plants and creatures is altogether extraordinary. In humans, transportation is brought out through the circulatory framework. This framework incorporates the heart, blood, and blood conveying veins.
- Digestion is the compound cycle wherein various kinds of substance responses are engaged with controlling the living condition of the cells in a living being.
- Respiration incorporates the trading of gases just as the consumption of food. Organisms have an all-around characterized respiratory framework for breath.
- Reproduction- The organic cycle of replicating their own posterity decides the coherence of species, many ages. The fundamental sorts of multiplication are sexual and agamic proliferation.
- Excretion- Disposal of harmful material substances from the body is called discharge. There are different methods of discharge and it by and large contrasts with the various kinds of living species
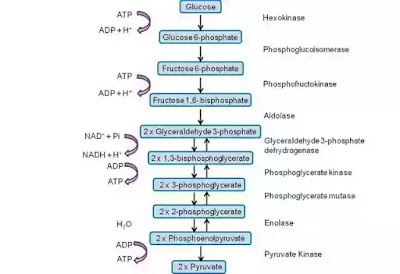
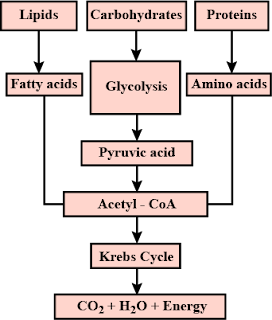
- Carbohydrates are the major sources of energy and this energy is produced in the form of ATP. Glucose which is a type of carbohydrate undergoes oxidation in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP. It undergoes three steps to get completely oxidised and the end products which are obtained are CO2, energy and water. Glucose may also undergo anaerobic respiration under certain circumstances.
- Proteins are biomolecules which are made up of several amino acids that are joined together by peptide bonds. For every 1 gram of protein which is digested 4 Kcal energy is released. Proteins are digested and broken down into amino acids which are then absorbed by the various cells of the body. These amino acids are then used for the synthesis of proteins required by cells and the body.
- Fats are molecules which are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. Digestion of fats yield fatty acids which are absorbed by the cells and used as per their requirement. For example, fatty acids are used for producing hormones like progesterone, estrogen etc.