5 Key Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord PDF Free
To people who are not familiar with the topic, it may seem that the terms “Brain” and “spinal cord” refer to the same part of the body. Although both are essential for the correct functioning of the body, the Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord are quite marked.
The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). The brain controls our thoughts, feelings, learning, and movements, as well as automatic functions like breathing and heart rate. It is safeguarded by the skull.
The spinal cord consists of nerves that run along the spine. It carries messages from the brain to different parts of the body. Starting at the base of the brain, it extends down to the lower back. The spine’s bones protect the spinal cord.
Both the brain and spinal cord are shielded by three layers of tissue called meninges. The space between two of these layers, known as the subarachnoid space, contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This fluid cushions the brain, supplies it with nutrients, and removes waste products.
What is the Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord
The brain is the center of emotions, memory, thought, vision, hearing, speech, and many other functions. The spinal cord and cranial nerves help carry messages between the brain and the rest of the body. These messages control muscle movements, transmit sensory information, and coordinate internal organ functions.
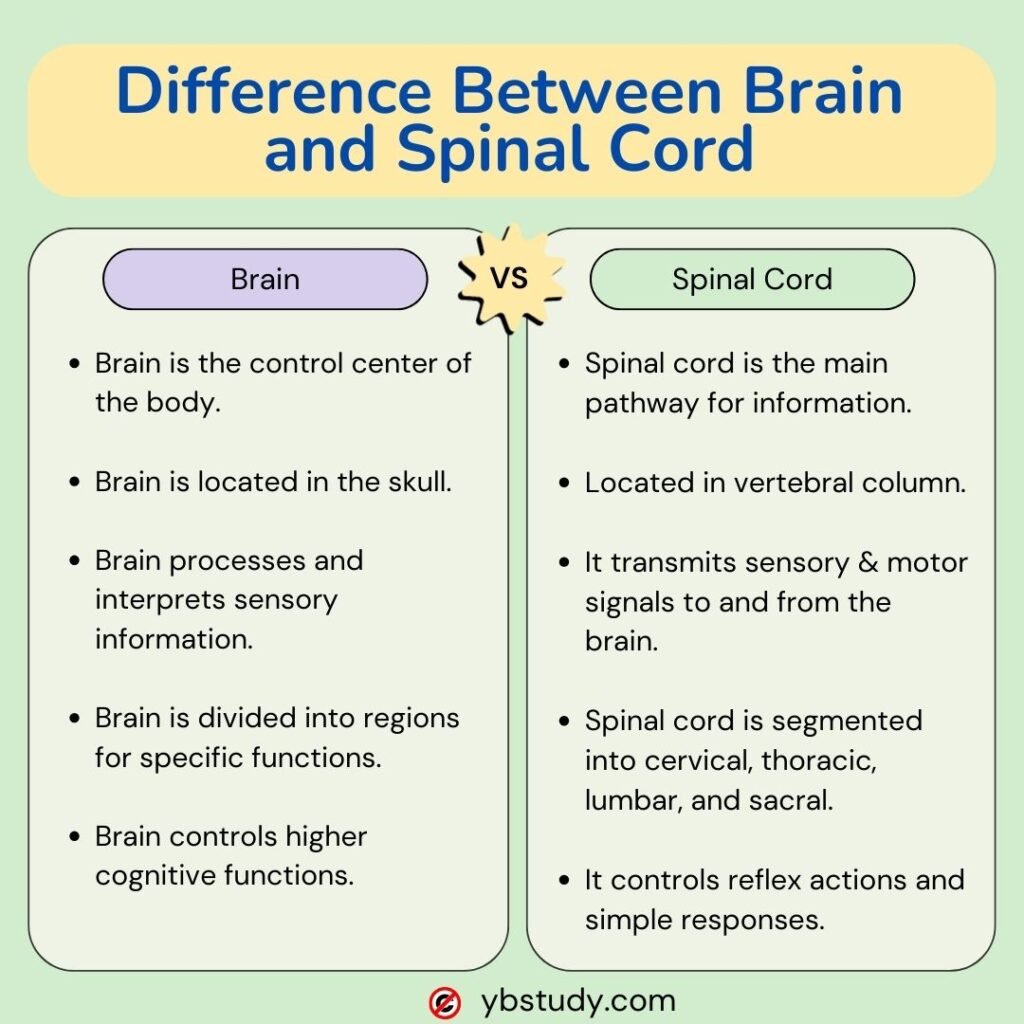
The brain is protected by the skull, and the spinal cord is protected by the vertebral column.
Both the brain and spinal cord are surrounded and cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is produced by the choroid plexus, located in spaces within the brain called ventricles. These ventricles and the spaces around the brain and spinal cord are filled with CSF, providing protection and support. Here below we have summarize the Key Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord in Table format.
| Brain | Spinal Cord |
|---|---|
| The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system located in the head. | The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem to the lower back. |
| The brain is protected by the Skull. | It is protected by the Vertebral column. |
| Divided into three parts: Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain | Divided into four regions: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral |
| It processes information received from sensory organs and controls responses to stimuli. | It primarily functions as a pathway for transmitting neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body. |
| The brain is the portion CNS ( Central Nervous System) that is located inside the skull. | It is a long thin tube-like structure |
| The brain is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, memory, and emotion. | The spinal cord primarily facilitates reflex actions and basic motor functions such as walking and reflex arcs. |
| It consists of different regions including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. | It is composed of nerve fibers that are grouped into tracts and surrounded by protective membranes called meninges. |
| The brain sends the command to different parts of the body. | It helps in transferring the signal of motion from the brain to different parts of the body. |
| Damage to the brain can result in diverse neurological deficits depending on the affected area. | Damage to the spinal cord can lead to paralysis or loss of sensation below the injury site. |
| Brain controls almost all body activities including thoughts, beliefs, memories, emotions, appetite, sensations, and involuntary actions | Carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body |
Read: 5 Key Difference Between Plants and Trees
5 Key Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord PDF Image
Read: 5 Key Difference between Adolescence and Puberty
What is the Brain?
The brain is a soft, spongy mass. It is protected by the bones of the skull and three thin membranes called the meninges. The brain is surrounded by a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This fluid is contained in the spaces between the membranes of the brain and in the cavities that are inside the brain called ventricles.
The neural network carries messages from the brain to the rest of the body and back. Some nerves extend directly from the brain to the eyes, ears, and other parts of the head. Other nerves pass through the spinal cord, connecting the brain to other parts of the body. Inside the brain and spinal cord, nerve cells are surrounded by glia cells, which also hold the nerve cells in place.
The brain controls what we want to do like talking or walking and what the body does without thinking like breathing. The brain also controls our senses like vision, hearing, touch, taste and smell), memory, emotions and personality.
Three main parts of the brain control different functions:
Forebrain: The forebrain is the largest part of the brain. It is located at the top of the brain and uses information from our senses to tell us what is happening around us and also gives orders to the body how to respond. It controls reading, thought processes, learning, speech and emotions. The forebrain is divided into left and right hemispheres, which control different functions. The right hemisphere controls the muscles of the left half of the body, the left hemisphere controls the muscles of the right half of the body.
Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located under the forebrain at the back of the brain. The cerebellum controls balance and complex functions such as walking and speaking.
Brain stem: The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls hunger and thirst, as well as breathing, body temperature, blood pressure and other basic body functions.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is an organ of the central nervous system. It is located in the spinal canal and 40–45 cm long. The spinal cord weighs approximately 30g. The spinal canal around the spinal cord contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The fluid fills the canal that runs through the center of the spinal cord. It ensures metabolic processes and softens mechanical effects during human physical movements.
The spinal cord begins at the brain at the level of the foramen magnum of the skull and ends in the lumbar spine. Below in the spine is the so-called equine tail, consisting of bundles of nerve fibers. The spinal cord is divided into two halves by two longitudinal grooves (anterior and posterior). The central part of the spinal cord consists of gray matter surrounded by white matter.
The white matter is formed by the processes of neurons and performs a conductive function – it ensures the transmission of impulses between the spinal cord and the brain and between different parts of the spinal cord.
FAQs on the Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord
1. What are the similarity and differences between Brain and Spinal Cord
Answer: Similarities: The spinal cord and brain make up the CNS (central nervous system). Without them, the life of the body is impossible. They consist of white (nerve fibers) and gray (clusters of neuron bodies) matter. Differences: they have fundamentally different structures. The brain is responsible for conditioned reflexes, and the spinal cord is responsible for unconditioned reflexes.
2. What is the difference between brain and spinal cord?
Answer: The brain controls how we think, learn, move and feel. The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and nerves throughout the body.
3. What organ protects the brain and spinal cord?
Answer: There are three layers of membranes known as the meninges that protect the brain and spinal cord. The delicate inner layer is the pia mater. The middle layer is the arachnoid, a spider web-like structure filled with fluid that cushions the brain. The strong outer layer is called the dura mater.
4. What is the difference between the bone marrow and the spinal cord?
Answer: The spinal cord is located within the spine and transmits nerve impulses throughout the body. On the other hand, bone marrow is the spongy tissue found inside the bones and is the place where blood is produced because it contains stem cells.
5. What is the distribution between the brain and the spinal cord?
Answer: The brain and spinal cord are covered and protected by three layers of tissue (membranes) called the meninges. The area between two of these layers is called the subarachnoid space . It contains a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that acts as a protective cushion for the brain.
6. What function do the brain and spinal cord perform?
Answer: Anatomy and functions of brain and spinal cord tumors
The brain controls many important functions in the body, such as emotions, vision, thinking, speech, and movement. The spinal cord connects the brain to nerves throughout most of the body. This allows the brain to send messages to the rest of the body.
