Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Pdf | Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cell
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Pdf | Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cell: All known unicellular and multicellular organisms are divided into two groups – prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic are two different types of cells and both are completely different from each other. In this cell biology article, we explain all the differences between Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells so that you can distinguish them perfectly in your preparation.
Before starting let us know about concepts of what is cells and the similarities between prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells possess some basic similarities and differences described in detail in the table given below:

Similarities Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell:
Apart from the differences seen, there are also some similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells :
- DNA is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Protoplasm is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Photosynthesis occurs in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Cell membranes are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- The cell wall is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The cell wall in prokaryotic cells is made of peptidoglycan and in eukaryotic cells, the cell wall is made of cellulose.
- The 70s ribosome is found in prokaryotic cells and the 80s ribosome is found in eukaryotic cells.
- Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are the basic and fundamental units of life on Earth. Thanks to them, every one of the different unicellular and multicellular organisms has been able to evolve and colonize the different habitats on the planet.
- Both types of cells are characterized by being structures delimited by membranes that inside retain their DNA or genetic information as well as different enzymatic machinery that allows them to develop their vital functions: feeding, growth, and reproduction.
- To survive and evolve, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells constantly convert energy from one form to another, in addition to maintaining a continuous relationship with their exterior, to respond to the different sources of chemical-biological information that they receive from the environment.
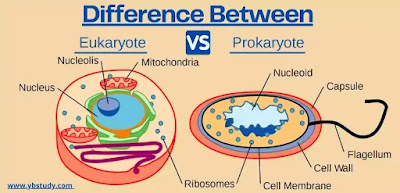
Difference Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|
| The Cell which carries a primitive or undeveloped nucleus is called a prokaryotic cell. | The cell which carries a true or developed nucleus is called a eukaryotic cell. |
| The size of the cell generally ranges from 0.2 micrometers to 2.0 micrometers in diameter | Eukaryotic cells range from 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter. |
| Simpler in structure | More complex in comparison to prokaryotic cells |
| The organelles in prokaryotic cells are not membrane-bound | The organelles in eukaryotic cells are certainly specific in function. Most noteworthy, they are membrane-bound |
| In this cell true nucleus is absent, instead, a nucleotide is present | The true nucleus is present. |
| DNA is arranged in a circular shape | DNA is linear in shape |
| In prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm is present, but it is lacking in most cell organelles. | In eukaryotic cells, it consists of both cytoplasm and organelles, both are present. |
| The cell wall is present here. Furthermore, it comprises mucopeptide or peptidoglycan | Usually, a cell wall is absent here. However, in case it is present, it comprises cellulose |
| Cell division occurs through binary fission, transduction, conjugation, and transformation | Cell division occurs through mitosis, Meiosis. |
| Mitochondria is absent | Mitochondria is present and it is a powerhouse of cells. |
| The endoplasmic reticulum is not present in prokaryotic cells. | The endoplasmic reticulum is present in eukaryotic cells. |
| The ribosome is present Smaller size 70S, distributed in the cytoplasm. | Larger size 80s, found on membranes as in endoplasmic reticulum; 70s present in organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondria. |
| Plasmids are commonly found in prokaryotes. | Plasmids are very rarely found in eukaryotes |
| In these cells, only asexual reproduction occurs. | Both sexual and asexual reproduction occurs. |
| These cells have a single origin of replication | These cells have multiple origins of replication |
| Only one chromosome is there in a prokaryotic cell. | There are many chromosomes present in the eukaryotic cells. |
| Bacteria and Archaea are the major examples of prokaryotic cells. | Plant cells and animal cells are the major examples. |
What is Cell
As we know the body of all organisms from the simplest to the most complex one is made up of many microscopic units which carry out the various processes that make the organisms living things. Such Basic structural and functional unit of the living body which are able independent existence is called a cell. All living things are composed of cells. A cell is the structural and functional unit of every living organism, capable of independent existence.
In living organisms, all functions are performed by the cell. Many organisms are Single cells called unicellular with the whole body comprising a single, free-living cell. These organisms are mostly microscopic, such as bacteria, Amoeba, Euglena, Chlamydomonas, etc. Other organisms (animals from sponges to mammals, most algae, fungi, plants, and trees) are multicellular (many cells). All these organisms differ in their structure, functions, and behavior. Since all life activities of an organism are present in miniature form in every cell, therefore, it is called a basic unit of life.
There are of two types cells based on the organization of DNA (nucleus), the organization of biomembranes, and a variety of membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles. These are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells contain 3 types of organisms blue green algae, bacteria, and PPLO (Pleuropneumonia like organisms) whereas the other organisms except the above three are included in eukaryotic cells.
The prokaryotic cells are morphologically the most primitive cells which means they lack true nuclei and membrane-bound cell organelles. They seem to have appeared about 3.5 billion years ago. A prokaryotic cell is essentially a single-membrane or one-envelope system. The membrane surrounds the cell. There is no membrane enveloping the genetic material and the membranes pervading the cytoplasm are scarce, if present they are usually associated with respiration or photosynthesis.
The eukaryotic cells have a more elaborate internal organization than the prokaryotic cells. A eukaryotic cell is essentially a double membrane or two-envelope system. The primary membrane surrounds the cell. Secondary membranes envelop the nucleus and certain other subcellular organelles and also pervade the cytoplasm. The eukaryotic cells occur in protists, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are called eukaryotes. The eukaryotic cells are of two types-plant animal cells. Most of the organelles and other structures of cells are common to animal cells and plants cell.
What are Prokaryotic Cells?
Prokaryotic cells have a relatively simple structure. A prokaryotic cell does not have a true nucleus, nucleolus, or chromosomes. Instead of a cell nucleus, there is a nucleoid (a nucleus-like structure) lacking a membrane and consisting of a single ring-shaped DNA molecule associated with a very small amount of protein. This is a cluster of nucleic acids and proteins located in the cytoplasm and not separated from it by a membrane. This is the decisive feature in dividing cells into prokaryotic (pre-nuclear) and eukaryotic (nuclear).
Prokaryotic cells do not have internal membranes, except for the dents of the plasma membrane. This means that they lack organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplasts, lysosomes, and the Golgi complex, which are surrounded by a membrane and are present in eukaryotic cells. There are also no vacuoles. Of the organelles, they only have ribosomes, which are smaller than those of eukaryotic cells. The cell wall of prokaryotic cell contains murein . Its molecule consists of parallel polysaccharide chains, linked to each other by short peptide chains.
The plasma membrane can bend inward into the cytoplasm, forming mesosomes. The membranes of mesosomes contain oxidation-reduction enzymes, and in photosynthetic prokaryotes, also the corresponding pigments (bacteriochlorophyll in bacteria, chlorophyll and phycobilins in cyanobacteria). Due to this, such membranes are able to perform the functions of mitochondria, chloroplasts and other organelles. Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes is carried out by simple cell division in half. Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea. Examples of prokaryotes: spirochetes, proteobacteria, cyanobacteria, crenarchaeota.
What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure, although they contain the same basic structural components (cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm) as prokaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells are divided into compartments (reaction spaces) by numerous membranes. In these compartments, various chemical reactions occur independently of each other simultaneously.
In a cell, the main functions are distributed between the nucleus and various organelles – mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi complex, etc. The nucleus, plastids and mitochondria are separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane . The cell nucleus contains genetic material. Plant chloroplasts mainly perform the function of capturing solar energy and converting it into the chemical energy of carbohydrates during photosynthesis, and mitochondria produce energy by breaking down carbohydrates, fats, proteins and other organic compounds.
The membrane systems of the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells include the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex, which are necessary for the implementation of vital processes in the cell. Lysosomes, peroxisomes, and vacuoles also perform specific functions. Only chromosomes, ribosomes, microtubules and microfilaments of non-membrane origin. Eukaryotic cells divide through mitosis.
