Explore the Differences Between Backbone and Spinal Cord?
In this article, we will discuss the What is backbone and Spinal cord, and the Differences Between Backbone and Spinal Cord, and much more. Additionally, we will cover some important questions related to this topic.
The spinal cord is a crucial part of the central nervous system that transmits nerve impulses from the brain to the body’s organs. It extends almost the entire length of the vertebral column, beginning just below the medulla oblongata.
The spinal cord’s interior features an H-shaped cross-section of gray matter, surrounded by white matter. The spine contains 31 pairs of nerves, each consisting of a sensory neuron and a motor nerve, which transmit messages to and from the brain. The spinal cord is responsible for reflex actions and controls the involuntary functions of internal organs.
Avoiding spinal cord injuries is essential because severe injuries can lead to paralysis and impair sensory and motor functions in various parts of the body.
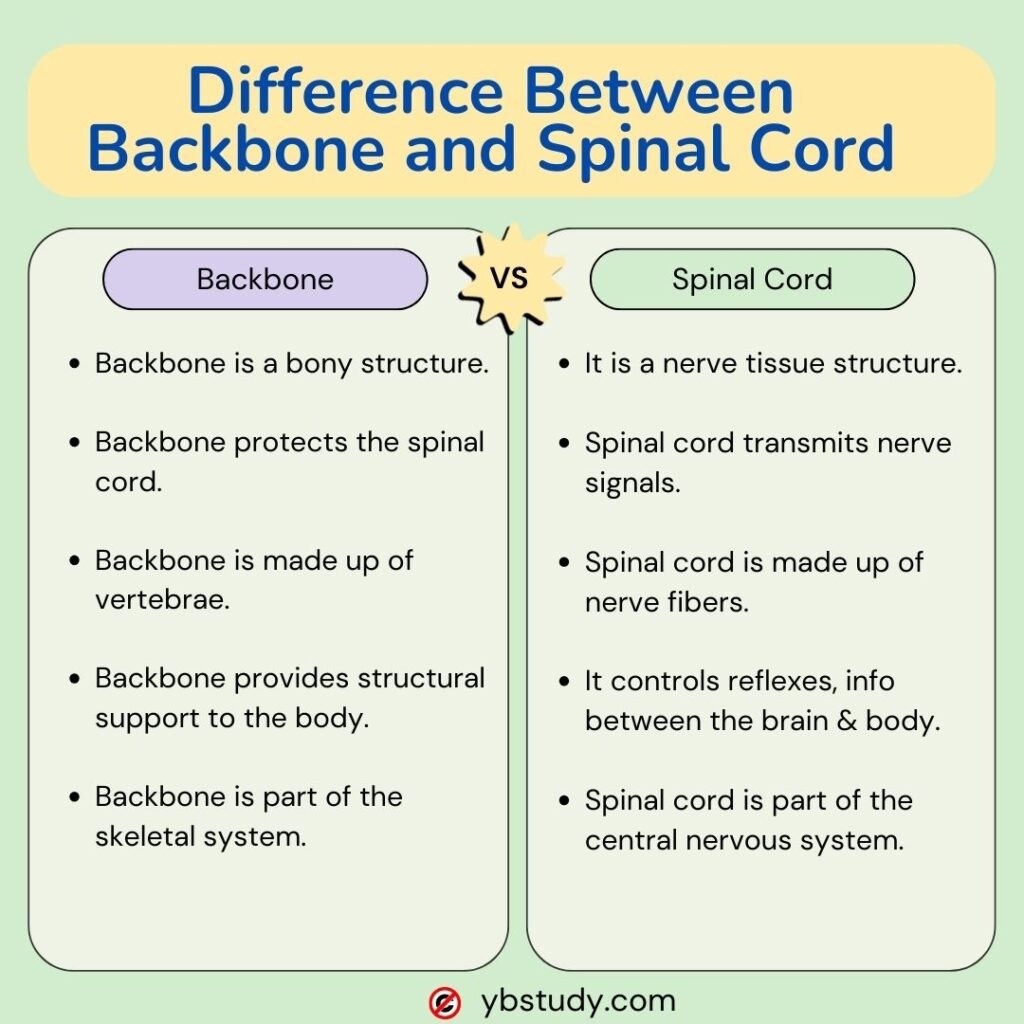
What are the Differences Between Backbone and Spinal Cord?
| Spinal Cord | Backbone (Vertebrae) |
|---|---|
| The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem down the vertebral canal of the backbone. | The backbone, or vertebrae, are the series of small bones that form the spine, providing structural support and protection to the spinal cord. |
| Made up of bundles of nerve fibres | The backbone is made of bones called vertebrae |
| It functions as a pathway for transmitting neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body, facilitating sensory and motor functions. | The backbone consists of individual vertebrae stacked on top of each other, separated by intervertebral discs that provide cushioning and flexibility. |
| Composed of nervous tissue and supportive cells | Composed of vertebrae, discs, ligaments, and muscles |
| The spinal cord is surrounded and protected by the vertebrae of the backbone, as well as by protective membranes called meninges. | The backbone forms the central axis of the body and supports the weight of the head, neck, and torso, while also allowing for movement and flexibility. |
| Damage to the spinal cord can result in paralysis or loss of sensation below the injury site, affecting motor and sensory functions. | Damage to the backbone, such as fractures or dislocations, can lead to pain, instability, and potential compression of the spinal cord or nerves. |
| Transmits nerve signals between the brain and body | Provides structural support and protection to the spinal cord and nerves |
| The spinal cord contains neural pathways that control reflex actions and convey sensory information to the brain for processing and response. | The backbone consists of different types of vertebrae (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal) that vary in size, shape, and function to support different regions of the body. |
| The spinal cord forms 31 segments, which are divided into 8 cervical nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 1 coccygeal nerve and 5 sacral nerves | The backbone can be split into 5 major segments – the cervical spine, the thoracic spine and the lumbar spine, the sacrum and the coccyx. |
Read: 5 Key Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord
5 Key Differences Between Backbone and Spinal Cord PDF Image
Read: 5 Key Difference Between Plants and Trees
What is the Spinal Cord?
The spinal cord is a vital part of the central nervous system that serves as a conduit for nerve impulses between the brain and the body’s organs. It controls many internal functions, including the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic viscera and blood vessels. The spinal cord is encased within the vertebral column and protected by three layers of meninges: the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. In humans, the spinal cord measures approximately 45 cm in males and 42-43 cm in females. It connects to the base of the brain at the brain stem and extends down to about two-thirds of the way down the backbone.
Read: 5 Key Difference between Adolescence and Puberty
What is the Backbone?
The backbone, also known as the vertebral column or spinal column, is a distinctive feature of vertebrates and a crucial component of the skeletal system. It provides structural support for the body and protects the spinal cord housed within it. The backbone connects to the skull at its superior end and to the pelvis at its inferior end. It comprises 33 individual bones called vertebrae, rather than being a single bone. The human backbone has four natural curves—cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral—that contribute to its flexibility and ability to support the spinal cord.
