Column Chromatography MCQ with Answers
Column chromatography MCQ: column chromatography is a chromatography method that is used to isolate a single chemical compound from a mixture and this process is used to separate substances based on differential adsorption of compounds to the adsorbent.
Column chromatography is a solid-liquid technique in which the stationary phase is solid and the mobile phase is a liquid. Column chromatography is used for the separation and purification of both solids and liquids.
The usual adsorbents employed in column chromatography are silica, alumina, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, magnesia, starch, etc.
This technique is widely applicable, as many different adsorbents in normal phase, reversed phase, or otherwise can be used with a wide range of solvents.
The technique can be used on scales from micrograms up to kilograms. The main advantage of column chromatography is the low cost over other stationary phases used in the process.
Using column chromatography all kinds of complex mixtures can be separated, Any amount of mixture can be separated by column chromatography.
Column Chromatography MCQ with Answers:
Here below we provide Column Chromatography MCQ with answers. Hope these solved Column chromatography MCQ questions will help, Engineering, Biotechnology, and Ph.D. students with UGC NET, SET competitive entrance, and University exam preparation. You can also read MCQ on Paper Chromatography.
1. Column chromatography is based on the principle of_______________
a) Ion-exchange
b) Exclusion principle
c) Differential adsorption
d) None of the above
Answer: C
2. Chromatography is a physical method that is used to separate__________
a) Simple mixtures
b) Complex mixtures
c) Viscous mixtures
d) Metals
Answer: B
3. Which force is involved in the Chromatography?
a) Hydrogen bonding
b) London force
c) Electric static force
d) All of the above
Answer: D
4. In which type of chromatography, the stationary phase is held in a narrow tube, and the mobile phase is forced through it under pressure?
a) Column chromatography
b) Planar chromatography
c) Liquid chromatography
d) Gas chromatography
Answer: A
5. In Column chromatography, the stationary phase is made of _________, and the mobile phase is made of _________
a) Solid, liquid
b) Liquid, liquid
c) Liquid, gas
d) Solid, gas
Answer: A
6. What is the factor responsible for the separation in column chromatography?
a) Polarity differences between the solvent
b) Polarity differences between the solute
c) Polarity indifference between the solvent
d) Polarity indifference between the solute
Answer: B
7. What is Eluent?
a) is a liquid solution
b) is a liquid solution that is a result of Elution.
c) It is a solvent used for the separation of absorbed material from the stationary phase.
d) None of the above
Answer: C
8. Which of the following is not a Column-type Liquid chromatography?
a) Gel permeation
b) Ion exchange
c) Liquid-solid
d) Paper
Answer: D
9. Which of the following is separated through column chromatography?
a) Chlorophyll and carotenoids
b) Inorganic cations or complexes
c) Sugar derivatives
d) Amino acids formed by hydrolysis of a protein molecule
Answer: A
10. Which of the following are the practical problems that arise due to the decrease in column diameter?
a) Requirement of large particle size and high-pressure drop
b) Requirement of large particle size and low-pressure drop
c) Requirement of small particle size and high-pressure drop
d) Requirement of small particle size and low-pressure drop
Answer: C
11. Which of the following statements about column chromatography is correct?
a) Resolution increases as the length of the column increases
b) The mobile phase is a porous solid material with appropriate chemical properties held in the column
c) The stationary phase is a buffered solution that percolates through the mobile phase
d) Large proteins emerge from the column sooner than smaller ones
Answer: A
12. Which of the following cannot be used as an adsorbent in Column adsorption chromatography?
a) Magnesium oxide
b) Silica gel
c) Activated alumina
d) Potassium permanganate
Answer: D
13. a______________ not done using column chromatography
a) Separation of inorganic cations or complexes
b) The identification of unknown compounds
c) Determination of the homogeneity of chemical substances
d) Separation of geometric isomers
Answer: A
14. The substance used as an adsorbent in the column chromatography is_________
a) Na²O
b) Na²SO⁴
c) Al²O³
d) alum
Answer: C
15. The principle of column chromatography is_________
a) Capillary action
b) Gravitational force
c) Differential absorption of the substance on the solid phase
d) Differential absorption of the substance on the phase
Answer: C
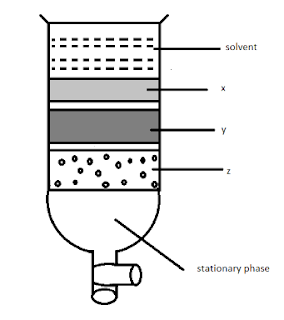
16. Column chromatography involves the separation of a mixture over a column of adsorbent (stationary phase) packed in a glass tube. Depending upon the degree of absorption complete separation takes place. In the given column, three colored bands x, y, and z are formed.
Identify the correct statement.
a) X, y, and z are absorbed to the same extent.
b) The most readily adsorbed component is retained near the top (x).
c) The most readily absorbed component comes down (z).
d) x, y, z layers are formed according to the wavelengths of the colors not on the basis of adsorption.
Answer: B
18. Two compounds I and II eluted by column chromatography (adsorption of I> II). Which one of the following is a correct statement?
a) II moves slower and has a higher Rf value than I.
b) II moves faster and has a higher Rf value than I.
c) I move faster and have a higher Rf value than II.
d) I move slower and has a higher Rf value than II.
Answer: B
19. The principle of column chromatography is:
a) Gravitational force
b) Capillary action
c) Differential absorption of the substances on the solid phase.
d) Differential adsorption of the substances on the solid phase
Answer: d
Hope the above Column Chromatography MCQ will help you…