5 key Difference Between Antigen and Pathogen PDF Download
There is a Difference Between Antigen and Pathogen, but the two are also closely related.
An antigen refers to the bacteria or virus itself that causes an infectious disease, but antigens are not limited to pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. An antigen is a general term for any substance that causes an immune response when it enters the body, such as pollen for people with hay fever or eggs for people with egg allergies .
Pathogens refer to microorganisms (including bacteria, viruses, rickettsia, fungi), parasites or other agents (recombinant microorganisms including hybrids or mutants) that can cause diseases in humans, animals or plants.
What is the Difference Between Antigen and Pathogen?
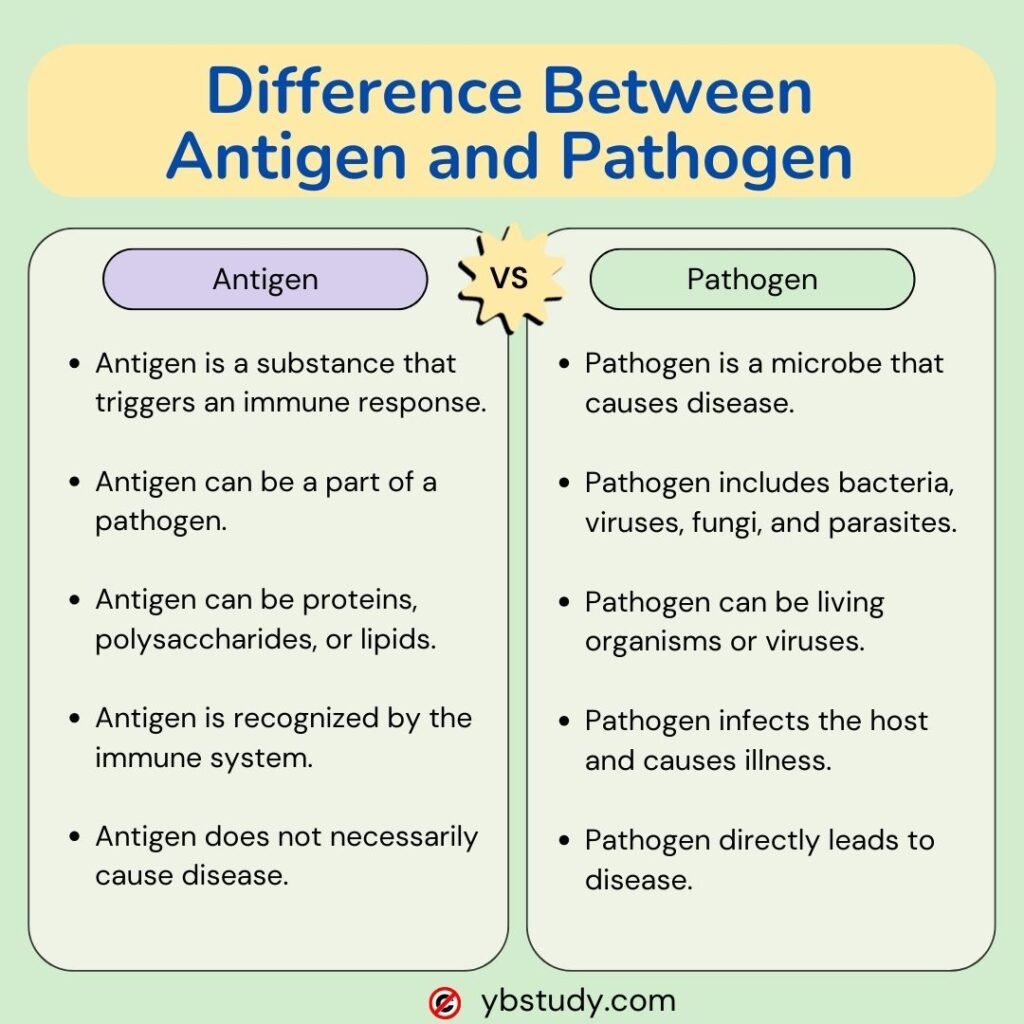
Antigen and pathogen are both important terms related to pathology and immunology. The main Difference Between Antigen and Pathogen are as follows:
| Antigen | Pathogen |
|---|---|
| An antigen is a sunstance that triggers immune responses; it’s often foreign to the body. | A pathogen is a agent that causes disease by invading and damaging host cells. |
| An antigen is a molecule | A pathogen is an infectious agent |
| Antigens are usually peptides or polysaccharides | Viruses, fungi, bacteria and other disease-causing microorganisms |
| Antigens are proteins or molecules on cell surfaces, helping the immune system identify threats. | Pathogens spread through air, water, or direct contact, leading to infections. |
| Sources of antigens can be of biological or non-biological origins. | Pathogens generally have biological origins – such as bacteria and fungi. It also includes non-living entities such as viruses and prions |
| Examples include viral proteins and bacterial cell components. | Examples include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. |
Read: Explore the Differences Between Backbone and Spinal Cord?
5 Key Difference Between Antigen and Pathogen PDF Image
Read: 5 Key Difference Between Brain and Spinal Cord
What is a pathogen?
A pathogen is an organism that enters the body and causes disease. Pathogens can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, or prions. Salmonella (bacteria), influenza virus, and malaria parasite are the best examples of pathogens. Pathogens cause disease in the body and cause damage to the body.
What is Antigen?
An antigen is a substance that activates the body’s immune system and stimulates a reaction. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, or nucleic acids. Examples of antigens are surface proteins of bacteria, outer coat proteins of viruses. The main function of an antigen is to develop an antibody or T-cell response to an antigen to protect against it.
