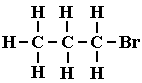Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Carbon Compounds Textbook Solutions
Maharashtra Board class 10 Chapter 9 Carbon Compounds textbook Solutions Pdf :
Our Science Chapter 9 Carbon Compounds class 10 questions and answers Pdf are highly effective for Maharashtra state board Exam. These Class 10 science Carbon Compounds Maharashtra Board Solutions is extremely helpful when you are preparing for class 10 exams.
Solving all the questions of Carbon Compounds chapter from the textbook without any trouble is a difficult task for class 10 science students. Most of the time Students get stuck with a particular Complex question. They try to attempt solving questions several times but are unable to find the correct answer. For these Our Class 10 Science textbooks Solutions have been studied & analyzed by ybsrudys experts and the solutions have been created as per the Maharashtra state board syllabus and students’ understanding. Students can easily access these useful Solution of 10th Class Science Carbon Compounds Class 10 Notes Pdf Download.
Cass 10 Science textbook Solutions will help a student to make a good score in their examination. So in order to help you with that, we have Compiled 10th Science Part 1 Chapter 9 exercise with answers for Class 10 below.
Important Points to Remember about Carbon Compounds:
- All the compounds having carbon as a constituent element are called as organic compounds. The compounds carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbide salts, carbonate salts and bicarbonate salts are exception; they are inorganic compounds of carbon.
- Generally the melting and boiling points of carbon compounds are found to be lower than 300°C.
- Generally most of the carbon compounds are found to be bad conductors of electricity. The chemical bond formed by sharing of two valence electron between the two atoms is called covalent bond.
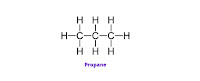
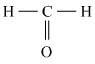
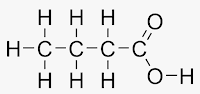
- The compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen as the only two elements are called hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are the simplest and the fundamental organic compounds. The smallest hydrocarbon is methane (CH4) formed by combination of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
- From the stuctural formula of ethane & propane it is seen that the valencies of all the atoms are satisfied by the single bonds. Such compounds are called saturated compounds.
- Ethane & propane are saturated hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbons are also called ‘Alkanes’.
- The carbon compounds having a double bond or triple bond between two carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds. Ethene and ethyne are unsaturated hydrocarbons. The unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon double bond are called ‘Alkenes’. The unsaturated hydrocarbons whose structures contain a carbon-carbon triple bond are called ‘Alkynes’.
Carbon Compounds Class 10 exercise with Answers :
Q.1: Match the pairs .
| Group A | Group B |
|---|---|
| a. C2H6 | 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbon |
| b . C2H2 | 2.Molecular formula of an alcohol |
| c. CH4O | 3.Saturated hydrocarbons |
| d. C2H6 | 4.Triple bond |
Answer :
| Group A | Group B |
|---|---|
| a. C2H6 | 1. saturated hydrocarbon |
| b . C2H2 | 2.Triple bond |
| c. CH4O | 3.molecular formula of an alcohol |
| d. C2H6 | 4.unsaturated hydrocarbon |
Q 2: Draw an electron dot structure of the following molecules. (Without showing the circles)
a. Methane
Answer :
b. Ethene
Answer :
c. Methanol
Answer:
Answer:
Answer :
Q.4 Explain the following terms with example.
a. Structural isomerism
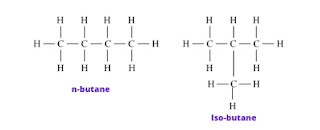
Answer: The phenomenon in which compounds having different structural formulae have the same molecular formula is called ‘structural isomerism. Butane and isobutane (C4H10) are structural isomers of each other.
Ex.
b. Covalent bond
Answer : The chemical bond formed by sharing of two valence electron between the two atoms is called covalent bond. A covalent bond is represented clearly by drawing an electron – dot structure. In this method a circle is drawn around the atomic symbol and each of the valence electrons is indicated by a dot or a cross. The covalent bond formed between the atoms is indicated by showing the circles around the atomic symbols crossing each other. The shared electrons are shown in the overlapping regions of the two circles by dot or cross. The electron – dot structure is also drawn without showing the circle. One pair of shared electrons constitutes one covalent bond . A covalent bond is also represented by a small line joining the symbols of the two atoms.
Ex.
H: H H-H
c. Hetero atom in a carbon compound
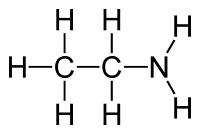
Answer :The atom of the element which is substitute for hydrogen is referred to as a hetero atom. Sometimes hetero atoms are not alone but exist in the form of certain groups of atoms. halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur. The atoms of these elements substitute one or more hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon chain and thereby the tetravalency of carbon is satisfied.
d. Functional group
Answer: The compound acquire specific chemical properties due to these hetero atoms or the groups of atoms that contain heteroatoms, irrespective of the length and nature of the the carbon chain in that compound. Therefore these hetero atoms or the groups of atoms containing hetero atoms are called functional groups. Common examples are alkane, Alkene, alkyne alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, ketones, and ethers,
e. Alkane
Answer: the valencies of all the atoms are satisfied by the single bonds. Such compounds are called saturated hydrocarbon .Saturated hydrocarbons are also called Alkanes .The general formula for alkane is CNH2N+2, where N is equal to no of carbon atom in a compound,which do not contain ring structures.
| CH4 | Methane |
| C2H6 | Ethane |
| C3H8 | Propane |
| C4H10 | Butane |
| C5H12 | Pentane |
| C6H14 | Hexane |
| C7H16 | Heptane |
| C8H18 | Octane |
| C9H20 | Nonane |
| C10H22 | Decane |
f. Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Answer: The carbon compounds having a double bond or triple bond between two carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds. Ethene (C2H3) and ethyne (C2H2) are unsaturated hydrocarbons. The unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon double bond are called ‘Alkenes’. The unsaturated hydrocarbons whose structures contain a carbon-carbon triple bond are called ‘Alkynes’. Generally the unsaturated compounds are more reactive than the saturated compounds.
g. Homopolumer
Answer: A homopolymer is a polymer formed from same type of monomer units. Common example of homopolymer is Polyvinylchloride (PVC), Polyethylene, Polystyrene etc.
h. Monomer
Answer: Macromolecule formed by regular repeatition of a small unit is called polymer. The small unit that repeats regularly to form a polymer is called monomer. ethylene, vinyl chloride, styrene are examples of monomer.
i. Reduction
Answer : The addition of hydrogen to a substance or removal of oxygen from a substance is called reduction.
For example:
2Ag2O → 4 Ag + O2 ↑
In a reaction, silver oxide is changing to silver. That is, oxygen is being removed from silver oxide. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so silver oxide undergoes reduction.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
In a reaction, copper oxide is changing to copper. That is, oxygen is being removed from copper oxide. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so copper oxide undergoes reduction.In a reaction, hydrogen is changing to H2O. That is,oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation, so hydrogen undergoes oxidation.
j. Oxidant:
Answer: The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an oxidising agent or oxidant. The substance which removes hydrogen is called an oxidising agent or oxidant.
For example:
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Oxidising agent=CuO
Reducing agent= H2
Substance oxidised=H2
Substance reduced=CuO
Q 5: Write the IUPAC names of the following structural formulae.
a. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
Answer : Butane
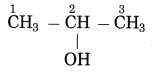
b. CH3-CH(OH)-CH3
Answer : Propan-2-ol
c. CH3-CH2-COOH
Answer : Propanoic acid
d. CH3-CH2-NH2
Answer : Ethan-1-amine
e. CH3-CHO
Answer : Ethanal
f. CH3-CO-CH2-CH3
Answer : Butanone
Q 6 : Identify the type of the following reaction of carbon compounds.
a. CH3 -CH2 -CH2-OH → CH3 -CH2 -COOH Answer : Oxidation reaction
b. CH3 -CH2 -CH3 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
Answer : Combusion reaction
c. CH3 -CH = CH -CH3 + Br2 → CH3 -CHBr – CHBr -CH3
Answer : Addition reaction
d. CH3 -CH3 + Cl2 → CH3 -CH2 -Cl + HCl Answer : Substitution reaction
e. CH3 -CH2 -CH2 -CH2 -OH → CH3 -CH2 -CH=CH2 + H2O
Answer : Dehydration reaction
f. CH3 -CH2 -COOH + NaOH → CH3 -CH2 -COO – Na+ + H2O
Answer : Neutralization reaction(reaction with base)
g. CH3 -COOH + CH3 -OH → CH3 -COO- CH3 + H2O
Answer : Esterification reaction
Q7: Write structural formulae for the following IUPAC names.
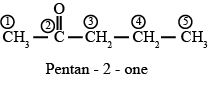
a. pent-2-one
Answer :
b. 2-chlorobutane
Answer :
c. propan- 2 ol
Answer :
d. methanal
Answer :
e. butanoic acid
Answer :
f. 1-bromopropane
Answer :
g. ethanamine
Answer :
h. butanone
Answer :
Q 8: Write answers as directed.
a. What causes the existance of very large number of carbon compound ?
Answer : Carbon has a unique ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms; this results in formation of big molecules. Being tetravalent one carbon atom can form bonds with four other atoms (carbon or any other). This results in formation of many compounds. These compounds possess different properties as per the atoms to which carbon is bonded.The carbon compounds contain open chains or closed chains of carbon atoms. An open chain can be a straight chain or a branched chain. A closed chain is a ring stucture.
b. Saturated hydrocarbons are classified into three types. Write these names giving one example each.
Answer: saturated hydrocarbons are classified into three types
1. straight chain hydrocarbon :
Ex. C3H4 propane
2. Branched chain hydrocarbon:
Ex. C4H10 Isobutane
3. Cyclic hydrocarbon :
Ex. C6H12 cyclohexane
c. Give any four functional groups containing oxygen as the heteroatom in it. Write name and structural formula of one example each.
Answer :
| Hetero atom | Name | Structural formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 1. Alcohol | – O – H | Methanol |
| 2. Aldehydes | O || – C – H | Acetaldehyde | |
| 3. Ketone | O || – C – | Acetone | |
| 4. Carboxylic acid | O || – C – O – H | Acetic acid | |
| 5. Ether | – O – | Dimethyl ether |
d. Give names of three functional groups containing three different hetero atoms. Write name and structural formula of one example each.
Answer :
| Hetero atom | Name | Structural formula | Condensed formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halogen (Class, Br, I) | Halo | -X (-cl, -Br, -I) | -X ( -Cl, -Br, -I) | CH3Cl-chloromethane CH3-CH2-Br-Bromoethane |
| Oxygen | Alcohol | -O-H | -OH | CH3-OH-methanol |
| Nitrogen | Amine | -N-H | H | NH2 | CH3-NH2- methyl amine CH3-CH2-NH2-ethyl amine |
e. Give names of three natural polymers. Write the place of their occurance and names of monomers from which they are formed.
Answer :
f. What is meant by vinegar and gashol? What are their uses ?
Answer : Vinegar is a kind of liquid that contains ethanoic acid, the acetic acid. Vinegar is produced by the fermenting ethanol via ethanoic acid in the presence of bacteria. Vinegar is used as a salad dressing, as a household cleaning agent, used to make pickles and so on. Gasohol is a combination of 90% alcohol and 10% Ethyl alcohol, also known as an alternative fuel or motor fuel. Gasohol is used in the automobile industry, used as common gasoline, also as a flexible fuel vehicle and more.
g. What is a catalyst ? Write any one reaction which is brought about by use of catalyst ?
Answer : Catalyst is a substance, which changes the rate of reaction, without causing any disturbance to it. Vegetable oil (unsaturated compound) undergoes addition reaction with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst to form vanaspati ghee (saturated compound).