Science Textbook solution for Class 7 Science chapter 2 Plant structure & functions
- The root, stem, leaves, flowers, fruits, etc. of different plants are different. The part that grows from inside the seed towards the soil is called the radicle and the part that grows above the soil is called the plumule.
- The root that forms from the radicle, grows into the ground. The root is thick near the ground and gradually tapers to a pointed end. This part of the plant growing below the soil for support is called ‘root’.Roots of some plants produce secondary ro
- ots; that grow obliquely and spread far and wide in the soil. Roots support the plant. This type of root is called a tap root.
Question 1: Give examples of 3 plants that have
a) spiny fruits
Answer : spiny fruits- jackfruit, breadfruit and custard apple
b) spiny stem
Answer : spiny stem- cactus, acacia and aloe vera
c) Red flowers
Answer : red flowers- rose, hibiscus and carnations
d) yellow flowers
Answer : yellow flowers- marigold, sunflower and daffodil
e) leaves which close at night
Answer :.leaves which close at night- acacia, mimosa and albizia
f) single seeded fruits.
Answer : single-seeded fruits- mango, plum, cherries
g) many-seeded fruits
Answer : many-seeded fruits- watermelon, apple and kiwi
Question 2 : observe any flower and write about parts of flowers.
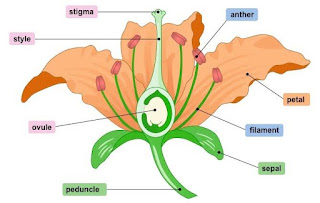
Answer : Flowers may have a long or a short stalk called pedicel. One end of the pedicel is attached to the stem. The other end of the pedicel is expanded and swollen. It is called the receptacle. Petals and other parts of the flower are supported on the receptacle. Calyx, corolla, androecium, gynoecium are different parts of a flower.
- Calyx : In the bud condition the petals are covered by leaf-like parts called sepals which are green in colour. They form the calyx.
- Corolla : This is made up of colourful parts called petals. Observe the shape, colour and smell of the corolla of various flowers like the rose, chrysanthemum, hibiscus, mogara, kanher, tagar, etc.
- Androecium : This is the male reproductive part of the flower. It consists of stamens. Each stamen is made up of anther and filament.
- Gynoecium : This is the female reproductive part of the flower. This is made up of carpels. A carpel consists of stigma, style and ovary.
Question 3: What are the similarities and differences between ?
a) jowar and moong
Answer : Jowar is a type of monocot plant and moong is a type of dicot plant. 2.Jowar has a fibrous root system and Moong has tap root system.
b) onion and coriander
Answer : Onion is a type of monocot plant and Coriander is a type of dicot plant.
c) leaves of banana and mango
Answer : Onion is a type of monocot plant and Coriander is a type of dicot plant.
Onion is a type of vegetable and Coriander is a type of herb.
d) coconut tree and jowar stalk plant
Answer : Leaves of coconut trees are arranged spirally and leaves of jowar stalk plants are arranged in opposite manner.
The height of coconut tree upto 23 meters and the height of the jowar stalk plant upto 3 meter.
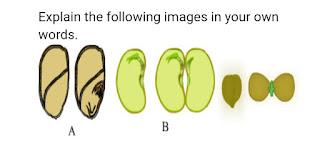
Question 4 : Explain the following images in your own words.
Answer :
Image A represents a cross section of a seed. The seed consists of seed coat, and an embryo. A seed coat is hard in nature and embryo is thick and swollen.
And image B represents a monocot and a dicot seed.
Question 5 : Describe the functions of various parts of a plant.
Answer : The different parts of a plants are-
1. Calyx.
2. Corolla.
3. Androecium.
4. Gynoecium.
1. Calyx:- In the bud condition the petals are covered by leaf-like parts called sepals which are green in colour. They form the calyx.
2. Corolla:- This is made up of colourful parts covered by leaf like parts called sepals. Observe the shape , colour and the smell of the corolla of various flowers like the rose, hibiscus, mogara, kankher, tagar etc.
3. Androcium:- This is the male reproductive part of a plant. It consists vof stamens. Each stamen is made up of another and filament.
4. Gynoecium:- This is the female reproductive part of a flower of a plant. This is made up of carpels. A carpel is consists of stigma, style, ovary.
5. Style:- It connects stigma to ovary.
6. Stigma:- It acts as a receptacle for the pollen grains.
7. Ovary:- It is the enlarged basal part on which style lies.
Question 6 : Certain properties are mentioned below. Find a leaf corresponding to each property and describe those plants. leaves with smooth surface, leaves with rough surface, fleshy leaf, spines on leaf.
1. Leaves with smooth surface:- The simple smooth edged leaves are 2 to 4 m long. The upper portion is green. E.g- Salix caroliniana.
2. Leaves with rough surface:- It is belonged to the category of shrubs. E.g- Asperiifolia.
3. Flashy leaf : A general definition of succulents is that they are drought resistant plants in which the leaves, stem or roots have become more than usually fleshy by the development of water-storing tissue.
Fleshy leaf are found in desert areas. Their leaves are green. Eg- opuntia.
4. Spines on leaves : Spines are modified leaves, stipules, or parts of leaves, such as extensions of leaf veins. Cacti often have a particular kind of spine (as found in areoles of Opuntia) called a glochidium or glochid (plural glochidia or glochids), which is very small and deciduous with numerous retrose barbs along its length.
Many plants have spices on their leaves. E.g- Acacia, aloe vera
Question 7 : Solve the following
Answer :
# Use your brain power
1) What would have happened if plants like tamarind, banyan and mango had fibrous roots?
Answer : Because fibrous roots are much thinner than tap roots and generally don’t grow as deep as tap roots. In addition, the fibrous roots may not find enough water, near the surface, to feed athe big trees.
2) What will happen if the root-tip is injured?
Answer : When the root tip gets injured, the root fails to penetrate the soil much. This means that the plant will get lesser nutrition from the soil. If the root fails to penetrate the soil, the plants do not get the required nutrition and thus the plant will not grow and may soon die
3) Which types of roots do the fenugreek, spinach and onion plants have ?
Answer : Feenugreek, Spinach and Onions have tap roots. A tap root is type of root which is dominant and large. It is very thick and straight and the other roots sprout from the tap root. Tap root is the first root to appear that goes deep down in to the soil.
4. What helps us to easily identify the plants around us?
Answer :Our eyes helps us to identify easily that the plant are around us.
5. Which are the various parts of plants?
Answer : A plant is made up of many different parts. The three main parts are: the roots, the leaves, and the stem. Each part has a set of jobs to do to keep the plant healthy
Tags : chapter 2 plant structures and functions answer key, multiple choice questions on plant structure and function, exam questions on plant structure and function, the plant structure and function, spiny fruits names, parts of a plant.