Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 -Animal classification Exercise
Animal classification chapter 6 Textbook Solutions :
Students can refer to the following animal classification chapter 6 textbook solutions for class 10 Science provided below based on the latest curriculum and examination pattern issued by Maharashtra state board. Our subject experts have prepared these questions and answers for class 10 students. which covers all topics from your textbook so that students can assess themselves on all important topics and thoroughly prepare for their board exams.
We have provided below animal classification chapter 6 class 10 notes Science with answers which will help the students to go through the entire syllabus and and practice textbook questions and answers provided here with solutions. You can download in Pdf Format and score high in your board exam you should go thorough all animal classification chapter 6 Class 10 solutions provided below so that you are able to get more marks in your exams
Important points to Remember about Animal classification
- Carolous Linneaus :he classified living things into two kingdoms- Plantae and Animalia.
- Ernst Haeckel: He proposed the three kingdom classification – Plantae, Animalia and Protista.
- Robert Whitakker: He gave the five kingdom classification- Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
- Carl Woese has also proposed the animal classification
- In case of multicellular animals, many cells are lperforming different functions in their body while in unicellular animals, as their body is made up of single cell; all functions are performed by same cell only.
- Asymmetrical Body : In case of such body, there is no any such imaginary axis of the body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Amoeba, Paramoecium, some sponges.
- Radial symmetry : In this type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis but any plane of body, it gives two equal halves. Ex. Star fish. In case of this animal, there are five different planes passing through central axis of body through which we can get two equal halves.
- Bilateral symmetry: In this type of body, there is only one such imaginary axis of body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Insects, fishes, frog, birds, human, etc.
a. I am diploblastic & acoelomate.
Which phylum do I belong to?
Answer: I am from phyllum Cnidaria.
Water vascular system is present in
my body. I am referred as fish though
I am not. What is my name?
phyllum Echinodermata
c. I live in your small intestine.
Pseudocoelom is present in my thread like body. In which phylum will you include me?
Answer: you included in phylum Aschelminthes and your name is Ascaris.
no tissues in my body. What is the
name of my phylum?
Answer: name of my phylum is Porifera
following animals with the help of
classification chart.
Bath sponge, grasshopper, rohu,
penguin, frog, lizard, elephant, jellyfish.
Kingdom: Animalia
Sub-kingdom: Non-chordata
Phylum: Porifera
- Level of organisation- cellular level
- symmetry – asymmetrical
- Coelom- Absent
- Notochord- absent
Kingdom: Animalia
Sub-kingdom: Non-chordata
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom- Coelomate
- Notochord- absent
Classification:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Pisces
Subclass: Teleostei
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom – Coelomate
- Notochord- present
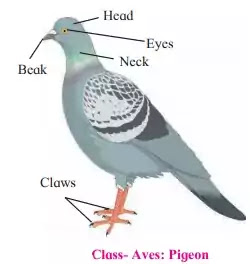
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom – Coelomate
- Notochord- present
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Amphibia
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom – Coelomate
- Notochord- present
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Reptilia
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom – Coelomate
- Notochord- present
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Characters:
- Level of organization – organ system
- Symmetry- Bilateral
- Coleom – Coelomate
- Notochord- present
Kingdom: Animalia
Sub-kingdom: Non-chordata
Phylum: Cnidaria or Coelenterata
Characters:
- Level of organization – tissue system
- Symmetry- radial
- Coleom – absent
- Notochord- absent
changes in animal classification.
Answer:
- Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first to perform the animal classification. Aristotle classified the animals according to the criteria like body size, habits and habitats.
- Further, as per the new Classification proposed by Aristotle is known as ‘Artificial method’.
- artificial method of classification was followed by Theophrastus, Pliny, John Ray, Linnaeus, etc. Later on,
- Natural system of classification’ was followed. Natural system of classification was based on various criteria like body organization, types of cells, chromosomes, bio-chemical properties, etc.
- Carolous Linneaus :he classified living things into two kingdoms- Plantae and Animalia.
- Ernst Haeckel: He proposed the three kingdom classification – Plantae, Animalia and Protista.
- Robert Whitakker: He gave the five kingdom classification- Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
- Carl Woese has also proposed the animal classification
4.What is the exact difference between
grades of organization and symmetry?
explain win examples.
Answer:
- In case of multicellular animals, many cells are lperforming different functions in their body while in unicellular animals, as their body is made up of single cell; all functions are performed by same cell only.
- Body organization of unicellular animals is referred as ‘Protoplasmic grade’ organization.
- In case of multicellular animals, if tissues are not formed, their body organization is called as ‘Cellular grade organization’. Ex. Phylum-Porifera.
- In case of some animals, cells come together to form tissues with the help of which all the body functions are performed. Such animals show ‘Cell – tissue grade’ organization. Ex. Animals from phylum- Cnidaria.Flat worms show ‘Tissue-Organ grade’ organization
- Remaining all animals show ‘Organ-system grade organization’ in which different organs are joined together to form organ-system that performs specific functions. Ex. Crab, Frog, Human, etc.
- Asymmetrical Body : In case of such body, there is no any such imaginary axis of the body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Amoeba, Paramoecium, some sponges.
- Radial symmetry : In this type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis but any plane of body, it gives two equal halves. Ex. Star fish. In case of this animal, there are five different planes passing through central axis of body through which we can get two equal halves.
- Bilateral symmetry: In this type of body, there is only one such imaginary axis of body through which we can get two equal halves. Ex. Insects, fishes, frog, birds, human, etc.
a. Give scientific classification of shark
upto class.
Answer: scientific classification of shark:
Phylum- Chordata
Sub- phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Pisces
of phylum- Echinodermata.
Answer:
- Calcareous spines are present on the body of these animals; hence they are called as echinoderms.
- These animals are found only in ocean.
- Their body is triploblastic, eucoelomate. And it is radially symmetrical in adult stage. However, they show bilateral symmetry in larval stage.
- They perform locomotion with the help of tube-feet. Tube feet are also useful for capturing the prey. Some animals are sedentary.
bat with the help of four distinguishing properties.
Answer:
| Bat | Butterfly |
|---|---|
| They are included in phylum mamalian . | They are included in phylum arthopods. |
| Body is divided in head, neck, trunck and fur. | These animal have jointed appendages. |
| Exoskeleton is in the form of hairs or fur. | Butterfly shows chitinous exoskeleton is presen their body. |
| Bat active at night. | Butterfly active during day. |
belong? Justify your answer with
scientific reasons.
Answer: Cockroach belong to phylun arthropods . It show following Characters:
- These animals have jointed appendages. Hence they are called as arthropods.
- Planet Earth has highest number of animals from this phylum. Hence, this is largest phylum with highly successful animals in animal kingdom.
- These animals are found in all types of habitats ranging from deepest oceans to highest mountains.
- Body of these animals is triploblastic, eucoelomate, bilaterally symmetrical and segmented.
- Chitinous exoskeleton is present around their body.
6. Give scientific reasons.
a.Though tortoise lives on land as well as in water, it cannot be included in
class- Amphibia.
Answer: Tortoise are classified under the class reptilia and not the class Amphibia as it has the following character:
contact with jelly fish.
Answer: Jellyfish belongs to the phylum Cnidaria. Cnidoblasts tentacles are present around the mouth. These tentacles are useful for capturing the prey whereas cnidoblasts inject the toxin in the body of prey. Those are useful for protection too. When its contact with the human skin it causes irritation.
chordates are not vertebrates.
Answer: Notochord present in of all chordates. The members of sub-phylum- Vertebrata possess notochord during the embryonic stage. But in adults the notochord is replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column. Whereas in member of other Sub-phyla of Chordata the notochord remain as such. But some chrodate’s like Urochordata and cephalochordata do not possess vertebral column and hence they are not vertebrates.
between non-chordates & chordates.
Answer: Balanoglossus is the connecting link between chordates and non-chordates Because notochord and pharyngeal characteristics are found in Balanoglossus. These characteristics are common to chordates. Dorsal heart is found in non-chordates. Balanoglossus also bears a dorsal heart. That’s why Balanoglossus have some characteristics of chordates as well as non-chordates. Hence it is the connecting link between chordates and non-chordates.
constant.
Answer: Body temperature of reptiles in not constant because Reptiles are cold blooded animals. Cold-blooded animals do not maintain a constant body temperature. They get their heat from the outside environment, so their body temperature fluctuates, based on external temperatures.
7. Answer the following questions by
choosing correct option.
a. Which special cells are present in
the body of sponges (Porifera)?
1. Collar cells. 2. Cnidoblasts.
3. Germ cells. 4. Ectodermal cells.
Answer: 1. Collar cells
b. Which of the following animals’
body shows bilateral symmetry?
1. Star fish. 2. Jelly fish.
3. Earthworm. 4. Sponge.
Answer: 3. Earthworm
regenerate it’s broken body part?
1. Cockroach. 2. Frog.
3. Sparrow. 4. Star fish.
Answer: 4. Star fish
1. Amphibia. 2. Reptilia.
3. Aves. 4. Mammalia.
Answer: 4. Mammalia
Hydra, Jellyfish, Planaria, Round worm, Butterfly, Earthworm, Octopus, Star fish, Shark, Frog, Wall lizard, Pigeon.
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-chordata
Phylum: Coelenterata
Example: Hydra
Classification:
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-chordata
Phylum: Coelenterata
Example: Jellyfish
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-Chordata
Phylum: Aschelminthes
Example: Roundworm
Classification:
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-chordata
Phylum: Arthopoda
Class: Insecta
Example: Butterfly
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-chordata
Phylum: Mollusca
Example: Octopus
Kingdom: Animalia
Division: Non-chordata
Phylum: Echinodermata
Example: Star fish
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub Phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Pisces
Example: Scoliodon (Shark)
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub Phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Amphibia
Example: Frog
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub Phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Reptilia
Example: Wall Lizard
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub-Phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Aves
Example: Pigeon
Answer: