Download CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus Pdf 2025
Class 12 Physics Syllabus: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has recently unveiled the new Class 12 Physics Syllabus for the upcoming academic session, 2025. Despite ongoing class 12 exams, this proactive move by the board aims to assist students transitioning into the new session with an updated curriculum. Providing early access to the CBSE syllabus allows students to effectively plan their studies and adapt to their new grade system.
In this article, we present the new CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus, which students can download from the direct links provided below. The syllabus covers various aspects of physics, offering insights into the course structure for the 2025 academic year.

Students can familiarize themselves with the chapters and topics they will study in physics. Additionally, the new CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus for 2025 also outlines the exam pattern and assessment criteria, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the curriculum.
The Senior Secondary stage of school education marks a transition from general education to a curriculum focused on discipline-based learning. The updated Class 12 Physics Syllabus aims to maintain a balance between the rigor and depth of disciplinary approach while ensuring it is comprehensible for learners. Care has been taken to align the Class 12 Physics Syllabus with international standards to enhance its quality and relevance. Key features of the updated Class 12 Physics Syllabus include:
- Emphasis on developing a basic conceptual understanding of the content.
- Utilization of SI units, symbols, nomenclature of physical quantities, and formulations in line with international standards.
- Logical sequencing of units to facilitate better understanding and linking of concepts.
- Reduction of curriculum load by eliminating overlaps between concepts within the discipline and with other disciplines.
- Promotion of process skills, problem-solving abilities, and practical applications of Physics concepts.
These features are designed to enhance the learning experience and prepare students for academic and professional pursuits in the field of Physics.
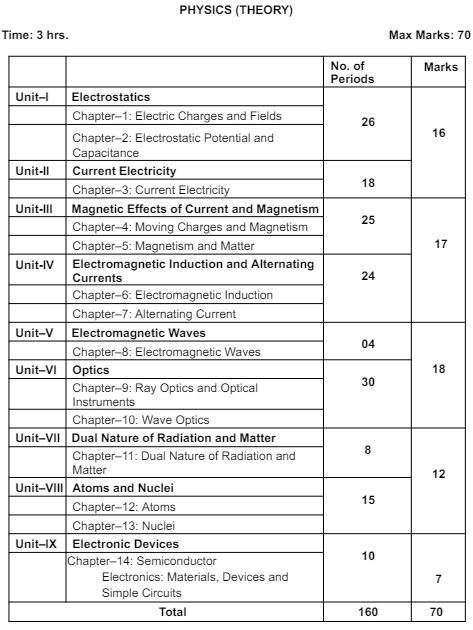
CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus Unitwise and Chapterwise
The curriculum for Class 12 Physics Syllabus aims to reinforce the concepts acquired during the secondary stage, laying a robust foundation for advanced learning in the subject. It endeavors to familiarize students with various processes employed in industrial and technological applications related to Physics.
Furthermore, the Class 12 Physics Syllabus focuses on cultivating essential skills such as experimental, observational, manipulative, decision-making, and investigatory skills among learners. It also strives to enhance problem-solving abilities and foster creative thinking.
Additionally, the class xii physics syllabus aims to develop conceptual competence in students, enabling them to recognize and appreciate the interconnectedness of Physics with other disciplines.
| Unit No. | Unit Name | No. of Periods | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Electrostatics | 26 | 16 |
| Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | |||
| II | Current Electricity | 18 | |
| Chapter 3: Current Electricity | |||
| III | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | 25 | |
| Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter | |||
| IV | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | 24 | |
| Chapter 6: Work, Energy and Power Chapter 7: Alternating Current | |||
| V | Electromagnetic Waves | 04 | 18 |
| Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves | |||
| VI | Optics | 30 | |
| Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Chapter 10: Wave Optics | |||
| VII | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 8 | 12 |
| Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | |||
| VIII | Atoms and Nuclei | 15 | |
| Chapter 12: Atoms Chapter 13: Nuclei | |||
| IX | Electronic Devices | 10 | 7 |
| Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits | |||
| Total | 160 | 70 | |
Class 12 Physics Chapters with IMP Points to Study
| Class 12 Physics Chapters | Important Points to Study |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields | Concept of electric charge and its properties – Coulomb’s law and its applications – Electric field and electric field lines – Electric flux – Gauss’s law and its applications |
| Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | Electrostatic potential and potential difference – Electric potential due to a point charge, due to a system of charges – Equipotential surfaces – Capacitors and capacitance |
| Chapter 3: Current Electricity | Electric current and its types – Ohm’s law and its limitations – Electrical resistance and resistivity – Kirchhoff’s laws and their applications – Potentiometer and its principle |
| Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism | Magnetic force on a moving charge in a magnetic field – Magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor – Biot-Savart law and its applications – Ampere’s law and its applications |
| Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter | Magnetic field intensity (H) and magnetic flux density (B) – Magnetic properties of materials – Classification of magnetic materials – Magnetic susceptibility and permeability |
| Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction | Electromagnetic induction and Faraday’s laws – Lenz’s law and its applications – Self-induction and mutual induction – Eddy currents and their applications – Alternating currents and voltage |
| Chapter 7: Alternating Current | AC generator and transformer – Peak and RMS value of AC – LCR series circuit and its resonance – Power in AC circuits – Power factor and its significance |
| Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves | Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics – Displacement current – Electromagnetic spectrum and its applications – Production and detection of electromagnetic waves |
| Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments | Reflection and refraction of light – Laws of reflection and refraction – Total internal reflection and its applications – Lens formula and lens maker’s formula – Magnification and optical instruments |
| Chapter 10: Wave Optics | Wavefronts and Huygens’ principle – Interference of light waves – Young’s double-slit experiment – Diffraction of light – Polarization of light and its applications |
| Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | Dual nature of radiation and matter – Photoelectric effect and its experimental setup – Einstein’s photoelectric equation and its applications – Particle nature of electromagnetic radiation |
| Chapter 12: Atoms | Atomic structure and Bohr’s model – Hydrogen spectrum and its significance – Dual nature of matter and De Broglie wavelength – Quantum mechanical model of the atom |
| Chapter 13: Nuclei | Composition and size of nucleus – Nuclear force – Radioactivity and its types – Decay law and half-life – Nuclear energy and its applications |
| Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits | Conductors, semiconductors, and insulators – Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors – p-n junction diode and its characteristics – Semiconductor diode as a rectifier – Special-purpose p-n junction diodes and their applications |
| Chapter 15: Communication Systems | Elements of a communication system – Basic terminology used in electronic communication systems – Modulation and its types – Amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM) – Communication satellites and their applications |
MCQ of Physics Class 12 Chapter wise with Answers Pdf
- Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields MCQs
- Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance MCQs
- Chapter 3: Current Electricity MCQs
- Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQs
- Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter MCQs
- Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction MCQs
- Chapter 7: Alternating Current MCQs
- Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves MCQs
- Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs
- Chapter 10: Wave Optics MCQs
- Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter MCQs
- Chapter 12: Atoms MCQs
- Chapter 13: Nuclei MCQs
- Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits MCQs
- Chapter 15: Communication Systems MCQs
Question Paper Design for CBSE Class 12 Physics
Here the below table provides a detailed breakdown of the question paper design for CBSE Class 12 Physics, including the type of questions, number of questions, marks per question, and total marks for each section.
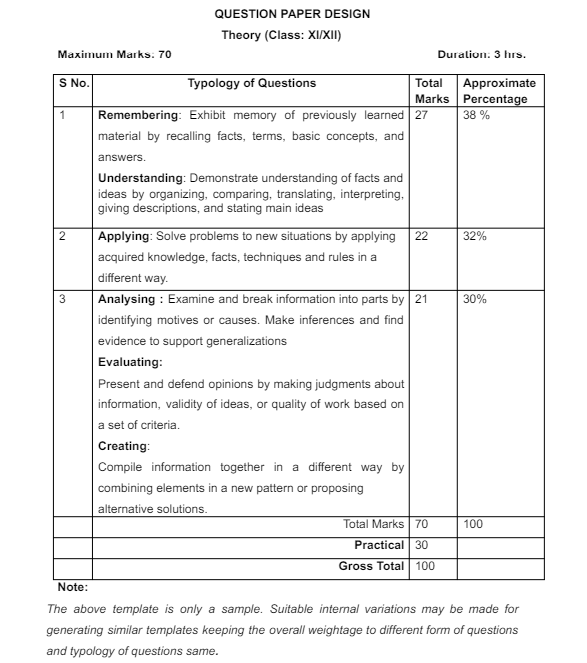
| Section | Type of Questions | Number of Questions | Marks per Question | Total Marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section A: Very Short Answer (VSA) | Objective Type Questions (1 mark each) | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| Total | ||||
| Section B: Short Answer I (SA I) | Short Answer Questions (2 marks each) | 7 | 2 | 14 |
| Total | ||||
| Section C: Short Answer II (SA II) | Short Answer Questions (3 marks each) | 12 | 3 | 36 |
| Total | ||||
| Section D: Long Answer (LA) | Long Answer Questions (5 marks each) | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| Total | ||||
| Total Marks | 27 | 70 |
Key Points about Class 12 Physics Syllabus:
- The question paper consists of four sections: A, B, C, and D.
- Section A contains very short answer type questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B contains short answer type I questions. Each question carries 2 marks.
- Section C contains short answer type II questions. Each question carries 3 marks.
- Section D contains long answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks.
- The total marks for the question paper is 70.
- Students are required to answer all sections.
