Download CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2025 Pdf Free
Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus: The Higher Secondary stage is pivotal in school education, marking the transition to specialized, content-oriented courses. After a decade of general education, students opt for Chemistry with aspirations of pursuing careers in basic sciences or professional fields like medicine, engineering, and technology.
The study of Chemistry at this stage equips learners with a conceptual foundation essential for tackling academic and professional challenges beyond the senior secondary level. To facilitate this journey, the CBSE has released the Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus, available for download in PDF format.

This comprehensive document outlines the chapters, practicals, projects, and assignments students need to cover for the academic year 2023-24. By systematically reviewing the Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus, students can effectively plan their studies and embark on a fulfilling academic journey in Chemistry.
Objectives of Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus
Here are the simplified objectives for the Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus at the Senior Secondary Stage:
- Help students understand basic chemistry concepts in an engaging way.
- Prepare students to study chemistry in college or for professional careers like medicine or engineering.
- Introduce students to new and important areas of chemistry and how they apply to real-world problems.
- Prepare students to tackle challenges related to health, nutrition, environment, population, weather, industries, and agriculture.
- Develop students’ problem-solving skills.
- Familiarize students with industrial processes and their practical uses.
- Show students how chemistry connects with other sciences like physics, biology, geology, and engineering.
- Teach students how chemistry relates to everyday life.
- Foster students’ interest in studying chemistry further.
- Integrate important life skills and values within the context of chemistry education.
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus Course Pattern
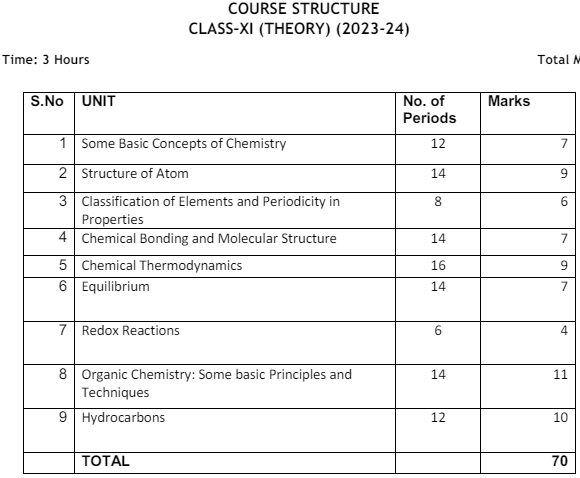
Revised Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus
The updated Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus adopts a disciplinary approach with rigor and depth, ensuring that the syllabus remains manageable while meeting international standards. Over the past decade, significant changes have occurred in the field of Chemistry, necessitating the inclusion of emerging areas such as synthetic materials, bio-molecules, natural resources, and industrial chemistry in the senior secondary syllabus.
International developments in formulations, nomenclature, and units of physical quantities, as endorsed by scientific bodies like IUPAC and CGPM, are also integrated into the updated syllabus. Emphasis is placed on new nomenclature, symbols, and formulations, as well as teaching fundamental concepts and their application to industry and technology. The revised Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus prioritizes logical sequencing of units, eliminates obsolete content, and minimizes repetition to optimize learning outcomes.
| Chapter Number & Name | Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus |
|---|---|
| 1. Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Importance of Chemistry, Nature of Matter, Laws of Chemical Combinations, Dalton’s Atomic Theory, Atomic and Molecular Masses, Mole Concept, Percentage Composition, Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry. |
| 2. Structure of Atom | Discovery of Subatomic Particles, Atomic Models, Thomson’s Model, Rutherford’s Experiment, Bohr’s Model, Quantum Mechanical Model, Dual Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation, de Broglie’s Equation, Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle, Quantum Numbers, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle, Hund’s Rule. |
| 3. Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Development of Modern Periodic Table, Periodic Trends in Properties of Elements (Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, Electron Affinity, Electronegativity), Periodic Classification of Elements, S-block, P-block, D-block Elements. |
| 4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Types of Chemical Bonds, Lewis Structure, Ionic and Covalent Bonding, Octet Rule, VSEPR Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Molecular Orbital Theory, Hydrogen Bonding, Geometry of Molecules, Polarity, Hybridization. |
| 5. States of Matter | Three States of Matter, Intermolecular Forces, Characteristics of Gases, Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, Gay-Lussac’s Law, Avogadro’s Law, Ideal Gas Equation, Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases, Real Gases, Deviation from Ideal Behavior, Liquid State, Surface Tension, Viscosity, Solid State, Types of Solids, Amorphous and Crystalline Solids. |
| 6. Thermodynamics | Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics, System and Surroundings, Types of Thermodynamic Processes, First Law of Thermodynamics, Enthalpy, Heat Capacity, Calorimetry, Second Law of Thermodynamics, Entropy, Gibbs Free Energy, Spontaneity, Thermochemical Equations, Hess’s Law, Enthalpy of Bond Dissociation and Combustion, Introduction to Entropy as a State Function, Gibbs Free Energy Change for Spontaneity. |
| 7. Equilibrium | Concept of Equilibrium, Equilibrium in Physical and Chemical Processes, Dynamic Nature of Equilibrium, Law of Mass Action, Equilibrium Constant, Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Equilibria, Le Chatelier’s Principle, Ionic Equilibrium, Acids, Bases, Ionization of Acids and Bases, Buffer Solutions, Solubility Equilibrium, Common Ion Effect, Hydrolysis of Salts, pH Scale. |
| 8. Redox Reactions | Oxidation and Reduction, Redox Reactions, Oxidation Number, Balancing Redox Reactions by Ion-electron Method, Redox Reactions in Terms of Half-reactions, Electrochemical Cells, Standard Electrode Potential, Nernst Equation, Electrochemical Series, Conductance in Electrolytic Solutions, Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis. |
| 9. Hydrogen | Position of Hydrogen in the Periodic Table, Dihydrogen, Preparation, Properties, and Uses, Heavy Water, Hydrogen Peroxide, Hydrides, Water, Structure, Properties, and Uses, Hard and Soft Water, Hydrogen as Fuel. |
| 10. The s-Block Elements | Group 1 and Group 2 Elements, Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals, General Characteristics, Electronic Configuration, Atomic and Ionic Radii, Ionization Enthalpy, Hydration Enthalpy, Chemical Reactivity, Anomalous Behavior of Lithium and Beryllium, Uses of Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals. |
| 11. The p-Block Elements | Group 13 to Group 18 Elements, General Characteristics, Electronic Configuration, Atomic and Ionic Radii, Ionization Enthalpy, Electronegativity, Physical and Chemical Properties, Oxidation States, Allotropes, Trends in Chemical Reactivity, Uses of Boron and Carbon. |
| 12. Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques | Organic Compounds, Classification, Nomenclature, Isomerism, Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism, Methods of Purification, Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis, Determination of Molecular Formula, Percentage Composition, Empirical Formula, Molecular Formula, and Structure of Organic Compounds, Elemental Analysis, Functional Group Analysis, Quantitative Elemental Analysis. |
Download Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus
Similar Articles
- CBSE Class 12 Biolog Syllabus 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2025
- Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- Updated CBSE Class 11 Biology Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Practical Syllabus 2025
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Practical Syllabus 2025
- NEET Syllabus for Beginners
